Information Bulletin JEE Main 2018 in English
Submission of Online Application Form: 01.12.2017 – 01.01.2018
Joint Entrance Examination (Main) – 2018
INFORMATION BULLETIN
JEE (Main) Secretariat
Central Board of Secondary Education
H-149, Sector – 63, Noida, Distt. Gautam Budh Nagar 201309 (UP)
DATE OF EXAMINATION
April 8, 2018(Sunday) (Pen & Paper Based Examination)
April 15th & 16th (Sunday & Monday) 2018(Computer Based Examination)
IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS
1. Candidates of JEE (Main) – 2018 have to apply online only. There is no printed application form for JEE (Main).
2. Please ensure that you are filling genuine application form available online at JEE (Main) website (www.jeemain.nic.in).
3. Please ensure your eligibility as per the criteria laid down for JEE (Main), JEE (Advanced) and participating State Institutions (as applicable).
4. The JEE (Main) secretariat/CBSE is only an examination conducting body. After declaration of result the data is handed over to SEAT ALLOCATION BOARD or the concerned state government/institute for Seat Allocation Process and admission procedure. The JEE (Main) Secretariat/CBSE does not collect the information regarding total number of seats available in the institutions and reservation criteria followed by the institutions.
5. All the candidates who have submitted the online application and paid the examination fee till last date will be allowed to appear in JEE (Main) and their admit cards will be uploaded on the website as per schedule. The JEE (Main) secretariat/CBSE do neither verify the information filled by the candidates in the application form nor verify any certificate of category/educational qualification for deciding the eligibility of candidates. The certificates of educational qualification and category (if applied under reserved category) will be verified by the concerned institution. The candidates are, therefore, advised to ensure their eligibility and the category (if applying under reserved category). The CBSE will, in no way, be responsible for any wrong/incorrect information furnished by the candidate(s) in their online application form. The letter/e-mails in this regard will not be entertained by JEE (Main) Secretariat/CBSE.
6. The use of Aadhaar for the candidates of JEE (Main) 2018 will result in accuracy of the candidates’ details. This will also help in ascertaining identities of the candidates at the examination centres in a convenient and hassle free manner. Aadhaar obviates the need for producing multiple documents to prove one’s identity.
7. The provisions of the Aadhaar Act and Regulations under the Act have come into effect from 14th September 2016 and notifications to this effect have been published in the Official Gazette. Section 57 of the Aadhaar Act 2016 permits the use of Aadhaar number for establishing the identity of an individual for any purpose pursuant to any law or any contract to this effect.
8. Accordingly, CBSE has decided to use Aadhaar for the candidates of JEE (Main) 2018, and hereby notifies the following:
7.1 Candidates, who are in possession of Aadhaar, shall enter Aadhaar number, name, date of birth & gender in online application for JEE(Main) 2018 for the purpose of his/her identity and authentication thereof.
7.2 Candidates not yet enrolled for Aadhaar, are hereby required to make application for Aadhaar enrolment in case he/she is entitled to obtain Aadhaar as per section 3 of Aadhaar Act. Such applicant may visit any Aadhaar enrolment centre (list available at www.uidai.gov.in) to get enrolled for Aadhaar.
7.3 The candidates who have enrolled for Aadhaar and have not received Aadhaar should enter 14 digit Aadhaar Enrolment ID (Including slash) printed on the Aadhaar enrolment slip at the time of filling online application form for JEE(Main) 2018.
8. The above provisions shall be applicable in all states except J&K, Assam & Meghalaya.
9. The candidates who have passed or appearing in Class XII examination from the states of J&K, Assam & Meghalaya need to enter the passport number, ration card number, bank account number or any other valid Govt. identity number provided they should select the city of examination in these states only.
10.The fee (in Indian Rupees) for JEE(Main)-2018 is as follows:
| Paper(s) Appearing | Pen and Paper Based Examination | Computer Based Examination (Paper-1 (B. E./B. Tech.)only) | ||
| (General/OBC) | (SC/ST/PwD) | (General/OBC) | (SC/ST/PwD) | |
| FOR EXAMINATION CENTRE OPTED IN INDIA | ||||
| JEE (Main) Paper-1(B.E./B.Tech.) orJEE (Main)Paper-2 (B. Arch./B. Planning) only |
1000 (Boys) 500 (Girls) |
500 (Boys) 500 (Girls) |
500(Boys) 250(Girls) |
250(Boys) 250 (Girls) |
| BothJEE (Main) Paper-1 (B.E./B.Tech.) and JEE (Main) Paper-2 (B.Arch./ B.Planning) |
1800 (Boys) 900 (Girls) |
900 (Boys) 900(Girls) |
1300 (Boys) 650(Girls) |
650 (Boys) 650 (Girls) |
| FOR EXAMINATION CENTRE OPTED IN FOREIGN COUNTRY | ||||
| JEE(Main)Paper-1 (B.E./B.Tech.)or JEE(Main)Paper-2 (B.Arch./B. Planning) only |
2500 (Boys) 1250 (Girls) |
1250 (Boys) 1250 (Girls) |
2500 (Boys) 1250 (Girls) |
1250 (Boys) 1250 (Girls) |
| Both JEE (Main) Paper-1 (B.E./B.Tech.) and JEE (Main) Paper-2 (B.Arch./ B.Planning) |
3800 (Boys) 1900 (Girls) |
1900 (Boys) 1900 (Girls) |
3800 (Boys) 1900 (Girls) |
1900 (Boys) 1900 (Girls) |
11. The fee may be paid either by credit/debit card or through e-challan generated during the online filling of the application form. In case of e-challan, the payment should be made in the Syndicate/Canara/ICICI Bank in cash. Please note that fee submitted by any other mode like money order, demand draft, IPO etc. will be rejected.Application fee once paid will not be refunded (full or partial) under any circumstances.
In case the examination fee is paid through credit/debit card, the candidates will need to pay an additional processing charge as following:-
Credit Card:-1.20% of the examination fee plus the GST as applicable.
Debit Card:- 0.75%+GST for examination fee upto Rs.2000 and 1%+GST for examination fee more than Rs.2000.
12. The candidates are required to check the status of fee payment at CBSE website (www.jeemain.nic.in) and if the status is ‘OK’ the candidate will be able to take the printout of Acknowledgement Page. In case, the fee payment status is not ‘OK’ the candidates are advised as following:-
i) If the fee is paid through e-challan by depositing cash in above mentioned bank, the candidate should contact immediately the concerned bank to update his/her fee status on the website.
ii) If the fee is paid through credit/debit card and status is not OK, it means the transaction is cancelled and the amount will, automatically, be refunded to concerned credit/debit card within 7 – 10 days. Therefore, such candidates have to pay the fee once again and ensure the OK fee status.
13.The candidates should select the cities of examination as per their choice of Paper -1or Paper – 2 or both Paper – 1 & Paper – 2 of JEE (Main) – 2018 according to the mode of paper(s) as following:
| CHOICE OF PAPER | MODE |
| PAPER -1 (B.E./B.TECH.) | PEN & PAPER BASED |
| COMPUTER BASED EXAMINATION | |
| PAPER-2(B.ARCH./B .PLANNING) | PEN & PAPER BASED |
| BOTH PAPER -1 (B.E./B.TECH.)&PAPER-2(B.ARCH./B .PLANNING) | PEN & PAPER BASED for both the Papers |
| COMPUTER BASED EXAMINATION for Paper – 1 and PEN & PAPER BASED for Paper – 2 |
Note: In the cities Bahrain, Dubai, Muscat, Riyadh, Qatar and Sharjah Paper – 1 will be conducted in both the modes, however, the candidates choosing the mode of Computer Based Examination for Paper–1 will appear for Examination only on 15thApril, 2018. The Paper–2 in all these cities will be conducted on 08/04/2018 from 2.00–5.00 PM (IST) in Pen & Paper Based examination.
14. Candidates are allowed to submit only one application form. More than one application i.e. Multiple applications from a candidate will be rejected.
15.The name of the candidate and his/her parents name in the application form must exactly be the same as registered in Class 12th/ equivalent qualifying Examination. No prefix/title such as Mr/Shri/Fr/Dr/Mrs/Smt/Col etc should be used.
16.No options can be changed at a later stage after submission of an application. However, a chance may be given to the candidates to correct/modify some of the particular(s)of the application form online only, with valid reason(s), after one week of closing date. The candidates are advised to see the website and newspaper regularly to know the exact date when the correction(s)/modification(s) will be allowed online only.
No change will be accepted through offline mode i.e. through fax/application including e-mail etc.
17. The JEE (Main) 2018 application has been made completely online i.e. the candidate have to fill the particulars online and also upload their photograph, signature and signature of father/mother/guardian. Due to above, the provision of sending hard copy of the application i.e. acknowledgement page to the JEE (Main) office has been done away with. Therefore the candidates are advised not to send hard copy of the application i.e. acknowledgement page to JEE (Main) Secretariat/CBSE.
However, the candidates are advised to retain hard copy of the application i.e. acknowledgement page for future reference or correspondence, if any.
18. Candidate(s) may check the status of their application on JEE (Main) website.
19. The Hon’ble High Court of Delhi alone will have the jurisdiction to settle and decide all matters and disputes related to JEE (Main)- 2018 as JEE Apex Board located at CBSE Delhi is organising the JEE (Main)- 2018 examination.
20. The offer of admission shall be subject to verification of original certificates/ documents at the time of admission. If any candidate is found ineligible at a later date even after admission to an Institute, his/her admission will be cancelled.
21. The candidates must have their own personal and valid email id. They are also advised to have their own mobile number. The candidates are advised to retain the same mobile number and email-id in use which they have furnished in the application form because the important information may be given to the candidates through SMS or e-mail.
22. The decision of the JEE Apex Board regarding the eligibility of any applicant shall be final.
23. All correspondence related to JEE (Main)–2018 should be addressed to:
The Executive Director, (JAB),
Central Board of Secondary Education,
H-149, Sector – 63, Noida
Distt. Gautam Budh Nagar 201309 (UP)
24. For latest information related to JEE(Main) – 2018 kindly visit JEE(Main) Website: www.jeemain.nic.in
25. For latest information related to JEE(Advanced) kindly visit the website www.jeeadv.ac.in
ABOUT PERCENTILE CALCULATION OF MARKS OF CLASS 12TH/QUALIFYING EXAMINATION
1. The percentage of marks and percentile are totally different entities hence the candidates should not confuse with both the above terms.
2. Percentage is a number out of 100.
3. Percentile Score of a candidate in a Board will reflect how many Candidates have scored below that candidate in his/her Board Examination.
A Percentile score is the value below which a certain percent of observations fall. For example, the 40th Percentile is the value or score below which 40 Percent of the observations may be found.
The Percentile of a Candidate will be calculated as
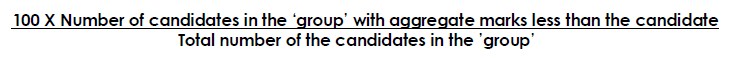
Example: Suppose in a particular Board:
No of Candidates Registered =13918 and No of Candidates Appeared = 13711
a. A Candidate who has scored 50% marks in the Board and 2218 candidates have scored below him; his Percentile score will be calculated as follows
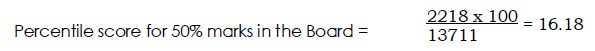
b. A Candidate who has scored 60% marks in the Board and 6865 candidates have scored below him; his Percentile score will be calculated as follows

c. A Candidate who has scored 90% marks in the Board and 13615 candidates have scored below him; his Percentile score will be calculated as follows

With these examples, it is clear that percentage of marks obtained by a candidate (50%, 60% or 90%) is different from the percentile score (16.18, 50.07 or 99.30).
4. The five subjects will be taken into account for calculation of percentile of qualifying examination marks for paper 1(B.E./B. Tech.)of JEE (Main) which are:
1- Language, 2. Physics, 3. Mathematics,
4-Any one of (Chemistry, Biology, Biotechnology, Technical Vocational Subject),
5- Any other subject.
Note: If a candidate has appeared in six subjects in the qualifying examination, the subject (fifth or sixth) with better marks will be considered.
5. For calculation of percentile of qualifying examination marks, for paper 2 (B. Arch./B. Planning) of JEE (Main), the marks obtained in following subjects will be considered:
1- Mathematics 2. Other four subjects.
6. For calculation of the total marks for five subjects, if the marks awarded in a subject is NOT out of 100, then the marks will be scaled (up or down) to 100 so that the total aggregate marks is out of 500.
7. For candidates who appeared in the Class XII (or equivalent) Board examination in 2017 but reappeared in 2018, the best of the two performances will be considered.
8. If a Board awards only letter grades without providing an equivalent percentage of marks on the grade sheet, the candidate should obtain a certificate from the Board specifying the equivalent marks and submit it at the time of acceptance of the allocated seat. In case such a certificate is not provided, the decision taken by the CSAB/JoSAA will be final.
9. If a Board gives aggregate marks considering both Class XI and Class XII examinations (in the 10+2 system), then only Class XII marks will be considered. Similarly, for Boards which follow a semester system, the marks scored in the final two semesters will be considered.
10. If a Board does not give marks scored in individual subjects but gives only the aggregate marks, then the aggregate marks given by the Board will be considered as such.
11. The category-wise cut-off marks for the top 20 percentile are calculated based on the marks scored by all the “successful” candidates in their respective boards in the particular year.
12. The cut-off marks for PwD candidates will be the same as the lowest of the cut-off marks for GEN, OBC-NCL, SC and ST categories.
13. It is reiterated that top 20 percentile cut-off for the academic year 2018 will be considered for the candidates who pass the Class XII (or equivalent) examination in 2018.
14. Similarly, top 20 percentile cut-off for the academic year 2017 will be considered for the candidates who pass the Class XII (or equivalent) examination in 2017.
15. If a candidate passes Class XII in 2017 but writes one or a few subjects in 2018 for improvement or any other reason, then top 20 percentile cut-off for 2017 will be considered. However, if a candidate writes all the subjects in 2018, then the best of the two performances will be considered.
16. In case a Board does not provide information about the cut-off for the top 20 percentile, the candidate will have to produce a certificate from the respective Board stating that he/she falls within the top 20 percentile of successful candidates. If the candidate fails to do so, then the cut-off marks for the CBSE will be used.
17. If a candidate passes Class XII (or equivalent) in 2017, but writes any of the required subjects (mentioned above) in 2018 for improvement or any other reason, then the aggregate percentage will be calculated by considering the maximum marks obtained in the required subjects.
18. For JEE (Advanced) 2018: Please visit JEE (Advanced) website www.jeeadv.ac.in for JEE (Advanced) 2018 criteria.
Contents
1. INTRODUCTION AND SCHEME OF EXAMINATION
2. ABOUT JEE (MAIN) – 2018
2.1 MODE OF EXAMINATION
2.2 TYPE OF EXAMINATION
2.3 SCHEDULE OF EXAMINATION
2.4 CHOICE OF MEDIUM OF QUESTION PAPERS
2.5 PROVISIONS FOR PERSONS WITH DISABILITES
2.6 CITIES/TOWNS OF JEE(MAIN) – 2018 EXAMINATION CENTRES
2.7 REQUEST FOR CHANGE OF EXAMINATION CITY/TOWN
2.8 USE OF CALCULATOR AND COMMUNICATION AIDS
2.9 ELIGIBILITY FOR APPEARING IN JEE (MAIN) – 2018
2.9.1 DATE OF BIRTH
2.9.2 YEAR OF PASSING QUALIFYING EXAMINATION (QE)
2.9.3 NUMBER OF SUBJECTS IN THE QUALIFYING EXAMINATION (QE)
2.9.4 NUMBER OF ATTEMPTS
2.9.5 NUMBER OF ATTEMPTS AND AGE LIMIT FOR THE STATES OF MADHYA PRADESH AND ODISHA
2.10 SCORE AND RESULT FOR JEE (MAIN) – 2018
3. ADMISSION TO NITS, IIITS, CFTIS, SFIS, STATE ENGINEERING COLLEGES FOR PARTICIPATING STATES AND OTHER PARTICIPATING INSTITUTIONS
3.1 ELIGIBILITY FOR ADMISSION TO NITS, IIITS AND OTHER INSTITUTIONS PARTICIPATING THROUGH CENTRAL SEAT ALLOCATION BOARD
3.2 ELIGIBILITY FOR ADMISSION TO OTHER INSTITUTIONS
3.3 NUMBER OF SEATS IN VARIOUS INSTITUTIONS
3.4 RESERVATION OF SEATS
3.5 SEAT ALLOCATION PROCESS AND ADMISSION PROCEDURE
4. ELIGIBILITY CRITERIA FOR APPEARING IN JEE (ADVANCED) – 2018*
5. APPLICATION PROCEDURE FOR JEE (MAIN) AND JEE (ADVANCED) – 2018
5.1 APPLYING ONLINE AND SUBMISSION OF APPLICATION
5.2 ONLINE APPLICATION FORMAT AND INSTRUCTIONS FOR APPLYING ONLINE
5.3 APPLICATION FORMAT
5.4 ADDITIONAL INFORMATION FOR CANDIDATES FOR JEE (ADVANCED) – 2018
6. ADMIT CARD FOR JEE (MAIN) – 2018
7. COMPUTER BASED EXAMINATION FOR PAPER-1 (B. E./B. TECH.) OF JEE (MAIN) – 2018
7.1 GUIDELINES TO CANDIDATES
7.2 INSTRUCTIONS FOR COMPUTER BASED EXAMINATION
8. PEN AND PAPER BASED EXAMINATION FOR PAPER-1 (B. E./B. TECH.) AND PAPER-2 (B. ARCH. / B. PLANNING) OFJEE (MAIN) – 2018
8.1 GUIDELINES TO CANDIDATES
8.2 INSTRUCTIONS FOR PEN AND PAPER BASED EXAMINATION
9. CODE OF CONDUCT FOR CANDIDATES DURING JEE (MAIN) – 2018
LIST OF APPENDICES
APPENDIX 1 SYLLABUS FOR JEE (Main) –2018
APPENDIX 2 LIST OF EXAMINATION CITIES FOR JEE (Main) – 2018
APPENDIX 3 LIST OF QUALIFYING EXAMINATIONS
APPENDIX 4 STATE CODE OF ELIGIBILITY
APPENDIX 5 TENTATIVE LIST OF PARTICIPATING INSTITUTIONS IN SEAT ALLOCATION BOARD
APPENDIX 6 BOARDS OF SCHOOL EDUCATION
APPENDIX 7 INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE OF TEST BOOKLET AND ANSWER SHEET (PEN AND PAPER MODE)
APPENDIX 8 TIME SCHEDULE FOR JEE (Main) – 2018
APPENDIX 9 PERFORMA OF DISABILITY CERTIFICATE
1. INTRODUCTION AND SCHEME OF EXAMINATION
Admission criteria to Undergraduate Engineering Programs at NITs, IIITs, Other Centrally Funded Technical Institutions, Institutions funded by participating State Governments, and other Institutions shall include the performance in the class 12/equivalent qualifying Examination and in the Joint Entrance Examination, JEE (Main). The Paper-1 (B. E./B. Tech.) of JEE (Main) will also be an eligibility test for the JEE (Advanced), which the candidate has to take if he/she is aspiring for admission to the undergraduate programmes offered by the IITs.
The States of Madhya Pradesh, Nagaland and Odisha have joined JEE (Main) system. Therefore, the candidates seeking admission to the institutions in these states, which were earlier admitting based on their State Level Examination, are also advised to fill in the JEE (Main) – 2018 application form online.
2. ABOUT JEE (Main)–2018
2.1 Mode of Examination
The Paper-1 (B.E./B. Tech.) (described below) of JEE(Main)will be conducted in two separate modes i.e. Offline (Pen and Paper Based Examination) mode and Online (Computer Based Examination) mode. The Paper-2 (B. Arch./B. Planning.) of JEE (Main) will be conducted only in Pen and Paper based examination mode. A candidate will opt for either Pen and Paper Based or Computer Based examination modes for Paper-1 (B. E./B. Tech.) only.
2.2 Type of Examination
JEE (Main) – 2018 shall have two papers, Paper-1 (B. E./B. Tech.) and Paper-2 (B. Arch./B. Planning.). Candidates may take Paper-1 (B. E./B. Tech.), or Paper-2 (B. Arch./B. Planning.), or both as per the course(s) they are seeking admission to. Subject combinations for each paper, type of questions in each paper and mode of examination available is given in the table below.
| SUBJECTS | TYPE OF QUESTIONS | MODE OF EXAM | |
| Paper 1 (B.E./ B. Tech.) | Physics, Chemistry & Mathematics | Objective type with equal weightage to Physics, Chemistry & Mathematics | Pen and Paper based OR Computer based |
| Paper 2 (B.Arch./ B.Planning) | Mathematics – Part I Aptitude Test – Part II & Drawing Test – Part III |
Objective type Objective type Questions to test drawing aptitude |
Only Pen and Paper based |
Requirement of papers for different courses is given in the table below.
| COURSE | PAPERS |
| All other undergraduate courses (B.E. /B. Tech.) | Paper –1 |
| B.ARCH/B. PLANNING(At Institutions other than IITs) | Paper –2 |
2.3 Schedule of Examination
A. Offline examination (Pen and Paper Based Examination) for Paper 1 (B. E./B. Tech.)and Paper 2 (B. Arch./B. Planning.)
| Date of Examination | Paper | Subjects | Timings | Duration |
| 08.04.2018 | Paper 1 (B.E./B. Tech.) | Physics, Chemistry & Mathematics | 0930-1230 Hours(IST) | 3 Hours |
| 08.04.2018 | Paper 2 (B. Arch./B. Planning) | Mathematics – Part I Aptitude Test – Part II & Drawing Test – Part III |
1400-1700 Hours(IST) | 3 Hours |
B. Online examination (Computer Based Examination) for Paper 1 (B. E./B. Tech.) Only
| Dates of Examination* | Paper | Subjects | Timings | Duration |
| 15/04/2018- (Sunday) 16/04/2018 – (Monday) |
Paper 1 (B. E./B. Tech.) | Physics, Chemistry & Mathematics |
1st shift 0930-1230 Hours (IST) 2nd shift (**)1400-1700 Hours (IST) **If required |
3 Hours |
*The option of date for Computer Based Examination for Paper – 1 should be exercised while filling up the application form. The allotment of slots/dates will be on first come first served basis. If a candidate does not make any selection, he/she shall be randomly assigned a slot/date as per the availability of the same.
The Computer Based Examination for Paper – 1 in Colombo, Dhaka, Kathmandu, Singapore, Bahrain, Dubai, Muscat, Riyadh, Qatar, Sharjah and Dhaka will be held on 15th April 2018.
In case a candidate, by furnishing the false information, appears in more than one slots/dates of the computer based examination or appears in both the modes of examination i.e. pen & paper based and computer based examination, his candidature will be cancelled and his result will not be declared.
2.4 Choice of Medium of Question Papers
| 1. | All Examination Centre Cities | English and Hindi Medium |
| 2. | Examination Centre Cities in Gujarat, Daman & Diu and Dadra and Nagar Haveli |
English, Hindi and Gujarati |
The option of question paper language should be exercised while filling up the Application Form and it cannot be changed at a later stage.
2.5 Provisions for Persons with Disabilities
- The candidates with disability should fill in the type and percentages of disability correctly in the online application form for JEE (Main) 2018.
- Only the visually challenged candidates, who have 40% or more disability, will be provided Scribe/Reader on the request of the candidate. In no case, the candidates will be allowed to bring their own scribe.
- Such candidate will have to submit the request to the centre superintendent for the same at least two days before the examination.
- The centre superintendent will identify the scribe/ reader students who are appearing in class X. In case a request is received from the candidate, he/she would be allowed to meet the scribe a day before the examination to verify the suitability of the scribe.
- One hour compensatory (extra) time will also be allowed to the candidates with 40% or more disability irrespective of the fact that the candidate(s) is/are availing the facility of scribe/reader.
2.6 Cities/Towns of JEE (Main)- 2018 Examination Centres
JEE (Main) – 2018 will be conducted in major cities and towns of India as well as abroad. The list of cities is given in Appendix-2. While applying, candidates must select four centre cities in case of Pen & Paper based examination and one city in case of Computer based examination. In case the candidate opting for Paper-I in the city where the examination is conducted only in computer based mode but also wants to appear in Paper-II, he/she has to select four other centre cities of pen & paper mode of examination for Paper-II.
However, if the number of candidates for Computer based examination is less than 50 in a city on a particular date than all such candidates will be allotted last day of the computer based examination in the same city.
Similarly, efforts will be made to allot candidate’s city of Pen & Paper based examination as per their choice opted for in the application form. However, in some exceptional circumstances, a different city in nearby area may be allotted.
2.7 Requests for Change of Examination City/Town
Normally, the requests for change of centre will not be entertained. In this regard, the decision of the Executive Director (JAB) will be final.
2.8 Use of Calculator and Communication Aids
Use of electronic devices like mobile phone, calculator etc. is NOT PERMITTED in JEE (Main) – 2018. Materials like log table, book, notebook, etc. should NOT be brought into the examination hall.
2.9 Eligibility for appearing in JEE (Main) – 2018
2.9.1 Date of Birth
Only those candidates whose date of birth falls on or after October 01, 1993 are eligible. However, in the case of Scheduled Caste (SC), Scheduled Tribe (ST) and Persons with Disabilities (PwD) candidates, upper age limit is relaxed by 5 years, i.e. SC, ST and PwD candidates who are born on or after October 01, 1988 are eligible. Date of birth as recorded in the Secondary Education Board/University certificate will only be considered.
2.9.2 Year of Appearance in Qualifying Examination (QE)
Only those candidates who have passed their Class 12th Exam or any equivalent qualifying examination in 2016 or 2017; or those who are appearing in their Class 12th Exam or any equivalent qualifying examination in 2018 are eligible to appear in JEE(Main)- 2018. Candidates who passed Class 12th/Qualifying examination in 2015 or before as well as those who will appear in such examination in 2019 or later are not eligible to appear in JEE (Main) – 2018. Candidates who appeared in class 12th/equivalent qualifying Examinations in 2015, did not pass in 2015, but passed in 2016 are also not eligible to appear in JEE (Main) 2018.
2.9.3 Number of subjects in the Qualifying Examination (QE)
Candidates must have taken at least five subjects in class 12th/qualifying examination in order to be eligible for writing JEE (Main) – 2018. The candidates who have taken four subjects are not permitted to write JEE (Main) 2018 and if such candidates appear in JEE(Main) 2018 by furnishing wrong information, their rank/result will not be declared.
2.9.4 Number of Attempts
The number of attempts which a candidate can avail at JEE (Main) shall be limited to 03 (three).
CANDIDATES ARE ALSO ADVISED TO NOTE AND VERIFY FOR THEMSELVES THE ELIGIBILITY FOR APPEARING IN JEE(ADVANCED) – 2018 AS WELL AS ELIGIBILITY FOR ADMISSION TO VARIOUS INSTITUTES. BEING ELIGIBLE TO WRITE JEE (Main) AND BY OBTAINING AN ALL INDIA RANK IN JEE (Main), A CANDIDATE DOES NOT AUTOMATICALLY BECOME ELIGIBLE FOR ADMISSION.
CANDIDATES SEEKING ADMISSION TO THE INSTITUTIONS IN THE STATES OF MADHYA PRADESH, NAGALAND AND ODISHA, WHICH WERE EARLIER ADMITTING BASED ON THEIR STATE LEVEL EXAMINATION, ARE ALSO ADVISED TO VERIFY THEIR ELIGIBILITY AS PER CRITERIA LAID DOWN BY THESE STATE GOVERMENTS.
2.9.5 No. of Attempts and Age limit for the states of Madhya Pradesh and Odisha:
Since the states of Madhya Pradesh, Nagaland and Odisha have joined JEE (Main) system from 2014. The age limit, for admission to institutions in these states which were earlier admitting candidates based on their state level examinations, will be as per their past practice only. The number of attempts in such cases will also remain same as per their past practice. This will however be obviously not applicable for admission to IITs/NITs/IIITs/CFTIs.
2.10 Score and Result for JEE (Main) – 2018
I. The score and rank of Paper-I of JEE (Main) – 2018 for all candidates will be declared by 30th April 2018. This score shall comprise the actual marks obtained in Paper-I of JEE (Main) – 2018 along with the status of those who qualify for appearing in JEE (Advanced) – 2018 provided and subject to other conditions of eligibility being met. The rank shall comprise All India rank and All India category rank.
II. Only the All India Rank (AIR) is used for admissions through Central Seat Allocation Board to NITs/IIITs/CFTIs/SFIs/Others, while other ranks are for information purposes.
III. No score/rank card will be dispatched to the candidates and the candidates are advised to download their score/rank cards from the JEE (Main) website http://jeemain.nic.in only.
IV. In case of a tie, i.e. when two or more candidates obtain equal marks, inter-se merit of such candidates shall be decided in the order mentioned under:
Rank list for admission to B.E. /B. Tech. (in institutions other than IITs)
· Resolution by marks obtained in Mathematics in JEE (Main) – 2018. Candidate obtaining higher marks will be given better rank.
· Resolution by marks obtained in Physics in the JEE (Main) – 2018. Candidate obtaining higher marks will be given better rank.
· Resolution by finding the ratio of positive marks and negative marks. Candidate having higher absolute value of the ratio will be given better rank.
· If the resolution is not possible after this criterion, candidates will be given the same rank.
Rank list for admission to B.Arch. /B. Planning (in institutions other than IITs)
· Resolution by marks obtained in Aptitude Test in Paper-2 (B. Arch./B. Planning.) in JEE (Main) – 2018. Candidate obtaining higher marks will be given better rank.
· Resolution by marks obtained in Drawing Test in Paper-2 (B. Arch./B. Planning.) in JEE (Main) – 2018. Candidate obtaining higher marks will be given better rank.
· Resolution by finding the ratio of positive marks and negative marks. Candidate having higher absolute value of the ratio will be given better rank.
· If the resolution is not possible after this criterion, candidates will be given the same rank.
V. The answer keys &images of response sheets (OMR sheets) of Pen & Paper Based examination and answer keys of Computer based examination will be displayed on the website www.jeemain.nic.in during 24th – 27th April, 2018. The candidates, who are not satisfied with the captured response, may challenge by filling online application form and paying a sum of Rs.1000/- per question The challenge of answer keys will also be accepted online only through the link available on the website www.jeemain.nic.in up to 11.59 PM on 27/04/2018 on payment of Rs.1000/- per question. The fee can be paid by credit/debit card. The fee once paid is non-refundable, however, in case the
challenge is accepted by the Board, the fee of Rs. 1000/- for each accepted challenge will be refunded to the concerned candidate. Such refund will be made online to the concerned credit/debit card account, so the candidates/parents are advised to use their own credit/debit card for making above payment. The JAB’s/CBSE’s decision on the challenges shall be final and no further communication will be entertained.
VI. All participating institutes that do not use the centralised Seat Allocation Process will prepare their own ranking based on the performance in JEE(Main)-2018 and other criteria as decided by them.
3. ADMISSION TO NITs, IIITs, CFTIs, SFIs, STATE ENGINEERING COLLEGES FOR PARTICIPATING STATES AND OTHER PARTICIPATING INSTITUTIONS
3.1 Eligibility for Admission to NITs, IIITs and CFTIs participating through SEAT ALLOCATION BOARD
Admission to NITs, IIITs and CFTIs participating though Central Seat Allocation Board will be based on All India Rank as explained above in section 2.10subject to the condition that the candidate should have secured at least 75% marks in the 12thclass examination, or be in the top 20 percentile in the 12th class examination conducted by the respective Boards. For SC/ST candidates the qualifying marks would be 65% in the 12thclass examination.
Subject combinations required in the qualifying examination for admission to B.E./B.Tech. & B. Arch./B. Planning Courses in NITs, IIITs, and other CFTIs shall be as under.
| Course | Required Criteria based on Class 12th / Equivalent qualifying Examination |
| B.E/B.TECH Passed | B.E/B.TECH Passed 10+2 examination with Physics and Mathematics as compulsory subjects along with one of the Chemistry/Biotechnology/Biology/ Technical Vocational subject. |
| B.ARCH./B.PLANNING | Passed 10+2 examination with Mathematics. |
3.2 Eligibility for Admission to Other Institutions
The above mentioned policy could also be adopted by other Technical Institutions participating in counselling through JoSAA/CSAB. In case a State opts to admit students in the engineering Colleges affiliated to state Universities, the State may prepare separate rank list based on criteria decided by them.
3.3 Number of seats in various institutions
For all admission related procedures/queries, the candidates are advised to refer the website of JoSAA, Central Seat Allocation Board (CSAB) or the concerned state government/institute after declaration of ranks of JEE (Main)– 2018. The letter/e-mails/grievances/RTI cases/Court cases regarding admission related procedures/queries will not be entertained by JEE (Main) Secretariat /CBSE.
3.4 Reservation of seats
As per Government of India rules candidates belonging to certain categories are admitted to seats reserved for them based on relaxed criteria. These categories are:
I. Other Backward Classes (OBC) if they belong to Non Creamy Layer (NCL)
II. Scheduled Castes (SC)
III. Scheduled Tribes (ST)
IV. Persons with Disability (PwD)with 40% or more disability
Benefit of reservation for admission to NITs/IIITs and CFTIs shall be given only to those classes/castes/tribes which are in the respective central list published by the Govt of India. For admission to State Engineering colleges who have opted for admission through JEE(Main)-2018, the reservation rules of that state shall apply. The letter/e-mails/grievances/RTI cases/Court cases regarding reservation criteria will not be entertained by JEE (Main) Secretariat/ CBSE.
3.5 Seat Allocation Process and Admission Procedure
Candidates shall be offered admission based on their choices and All India Ranks of JEE (Main)-2018 through a Seat Allocation Process to be announced later. The candidates will be able to make their choices online for branches/programmes and institutes at appropriate time.
Candidates are advised to regularly visit the JEE(Main) website http://jeemain.nic.in for latest information.
The verification of documents would be done at the time of Seat Allocation Process/admission. The purpose would be to verify different records regarding identification, age, qualifying examination, state of eligibility, category and disability (if any) of the candidate. On failing to produce any of the authentic documents, the candidate will not be considered for admission.
SC, ST, OBC and PwD candidates will be required to produce original certificate issued by the competent authority at the time of Seat Allocation Process as well as at the time of admission, failing which they will not be considered for admission.
4. ELIGIBILITY CRITERIA FOR APPEARING IN JEE (Advanced) –2018¹
The minimum academic qualification for appearing in JEE (Advanced) -2018 is that the candidate must have passed in final examination of Class 12thor equivalent qualifying examination (Appendix– 3).Those appearing in these examinations in 2018 can also appear in JEE (Advanced)- 2018 provisionally.
All the candidates aspiring to take admission in the undergraduate programmes at IITs and ISM Dhanbad for the year 2018 will have to appear in the Paper 1 (B. E./B. Tech.) of JEE (Main)-2018 Based on the performance in Paper 1 (B. E./B. Tech.) of JEE (Main)-2018, top 2,20,000 candidates (including all categories) will be eligible to appear in JEE(Advanced)-2018.
Admissions to IITs/ISM Dhanbad will be based only on category-wise All India Rank (AIR) in JEE (Advanced), subject to conditions as defined in JEE (Advanced)–2018 website.
A candidate can attempt JEE (Advanced) a maximum of two times in consecutive years irrespective of whether or not he/she passed the Qualifying Examination. The candidates, who have attempted JEE (Main) /JEE (Advanced) in 2016 or earlier, are NOT ELIGIBLE to appear in JEE(Advanced)–2018.
The candidate who had taken admission in any institute other than IITs & ISM Dhanbad in 2017 is eligible to appear in JEE (Advanced)–2018 provided that the candidate satisfies other eligibility criteria.
5. APPLICATION PROCEDURE FOR JEE (Main) AND JEE (Advanced) –2018
In order to appear in JEE (Main) and JEE (Advanced) 2018, the candidates are required to apply only online as per procedure detailed below².
5.1 Applying Online and Submission of Application
The online submission of particulars, uploading of scanned photograph and signatures may be made at JEE (Main) website. The candidates should supply all the required details while filling up the online form. On submission of details, a Acknowledgement Page with Application No. shall be generated.
Candidates are required to take printout of Acknowledgement Page and keep it for reference. The Acknowledgement Page is not required to be sent to JEE (Main) Secretariat/CBSE (please refer point no. 10 of Important Instructions on page 3). The application fee payment can be made:
(a) by credit/debit card/Paytm or
(b) by depositing fee in cash in the Syndicate/Canara/ICICI bank through e-challan generated during the online filling of application form.
5.2 Instructions for Applying Online
Before filling up the application form the candidate should have a scanned image of his/her photograph, signature and father’s/mother’s/guardian’s signature. These scanned images are to be uploaded during the submission of application form. The photograph should be colour or b/w (but clear contrast) with name of the candidate and date of taking the photograph printed on it as shown below. It should be without cap or goggles. Spectacles are allowed. Polaroid photos are not acceptable. Candidates with unclear photograph are liable to be rejected. Candidates may keep 6-8 identical photographs in reserve for use at the time of entrance examination, Seat Allocation Process and Admission.

¹Please refer to JEE (Advanced) website for the latest information and section 2.10(I) of the brochure.
²Please also see section 5.4 for JEE (Advanced)
The information given in the first column of the following table will be asked in the Online Application form. The instructions to fill up the form have been given in the second column.
5.3 Application Format
| AADHAAR Authentication | |
| Nationality | Indian / OCI/PIO/ Foreign |
| State of Eligibility | State from where the candidate has passed/appearing in class XII or equivalent examination or state mentioned in the Passport (Appendix 4) |
| State from where the candidate has passed/appearing in class XII or equivalent examination |
|
| State mentioned in the Passport | |
| Aadhaar Number, Aadhaar Enrolment ID, Aadhaar Registration number, Passport Number, Ration Card Number, Bank Account Number, any other valid Government ID Number |
|
| Candidate’s Name | As per Aadhaar or other ID |
| Date of Birth (DD/MM/YYYY) | As per Aadhaar or other ID |
| Gender | Male / Female/ Transgender (as per Aadhaar or other ID) |
| Examination Details JEE (Main) – 2018 | |
| Applying for | JEE (Main) Paper – 1 (B.E. / B. Tech.)Only JEE (Main) Paper – 2 (B. Arch. / B. Planning) Only JEE (Main) Paper – 1 & Paper –2 Both |
| Mode of Examination | Pen and Paper Based Examination Computer Based Examination |
| Choice of Examination Centre (any four) | As per list of Examination cities (Appendix 2) |
| Question Paper Medium | English / Hindi / Gujarati |
| Personal Details | |
| Mother’s Name | Maximum 46 Character |
| Father’s Name | Maximum 46 Character |
| Category | General/ SC/ ST/ OBC – NCL(Central List) State list OBC Candidates who are not in OBC – NCL central list must choose General. State admission boards shall verify State OBC list separately. |
| Person with Disability (PwD) | Yes/ No |
| If PwD, mention the percentage of disability? |
|
| Whether you need scribe/reader? | Yes/No |
| Place of Residence | Rural / Urban |
| Complete Mailing Address | |
| Pin code of mailing address | |
| Academic Details | |
| Year of Passing Class 10th or its Equivalent | 2002-2016 |
| Place of 12th class schooling | Village / Town / City |
| Year of Passing or Appearing Class 12th / Qualifying Examination |
2016 / 2017 / 2018 Note: Candidates from Madhya Pradesh and Odisha please see section 2.9.5 |
| School Board of Class 12th / Qualifying Examination |
As per list of Boards given in Appendix 6 |
| Roll Number of Class 12th / Qualifying Examination (if allotted) |
|
| Whether appearing for improvement examination of class 12th |
Yes/No |
| If, yes, Roll Number of improvement Examination (if allotted) |
|
| Name of the Qualifying Examination passed/appearing |
as per Appendix 3 |
| Type of Institution of Class 12th / Qualifying Examination |
Government / Private |
| Mode of Preparation | Self Study / Individual Tuition / Coaching/ Correspondence Courses/Others |
| Name & Address of the School / College from where passed / appearing |
|
| Contact Details | |
| Email Address | |
| Mobile No. | |
| Land line no. with STD code or any other contact no. |
|
| Guardian Details | |
| Father’s Qualification | Illiterate / Matriculate / Graduate / Post Graduate / Others |
| Father’s Occupation | Agriculture/ / Business/ Medical/ Engineering /Law Practice/ Government Service/ Public Sector Service/ Private Service/ Teaching or Research/ Architecture/ Pharmacy/ Self Employment/Others (including House wife) |
| Father’s Annual Income | Up to 100000 /Rs. 100001 -200000 / Rs. 200001 – 300000 /Rs. 300001 -400000 / Rs. 400001 -500000 /Rs. 500001-600000 / Rs. 600001-700000 /Rs. 700001-800000 / Rs. 800001 and above |
| Mother’s Qualification | Illiterate / Matriculate / Graduate / Post Graduate / Others |
| Mother’s Occupation | Agriculture/ / Business/ Medical/ Engineering /Law Practice/ Government Service/ Public Sector Service/ Private Service/ Teaching or Research/ Architecture/ Pharmacy/ Self Employment/ Others (including House wife) |
| Mother’s Annual Income | Up to 100000 /Rs. 100001 -200000 / Rs. 200001 – 300000 /Rs. 300001 -400000 / Rs. 400001 -500000 /Rs. 500001-600000 / Rs.600001-700000/Rs.700001-800000/Rs.800001and above |
| Declaration by the candidate | I hereby declare that all the particulars stated in this application form are true to the best of my knowledge and belief. I have read and understood the JEE procedures for both JEE (Main)- 2018 and JEE(Advanced) – 2018. I shall abide by the terms and conditions thereon. If any data is found to be false, I understand that I will be disqualified. |
| Declaration by Father/Mother/Guardian | I hereby declare that I have verified the data submitted by my ward. If any data is found to be false, I understand that my ward will be disqualified. |
| To be uploaded during the submission of online application form | |||
| File Format | File Size | Dimension | |
| Photograph of Candidate | JPEG format | 4KB to 40KB | 3.5cm x 4.5cm |
| Signature of Candidate | JPEG format | 1KB to 30KB | 3.5cm x 1.5cm |
| Signature of Father/Mother/Guardian | JPEG format | 1KB to 30KB | 3.5cm x 1.5cm |
5.4 Additional Information for Candidates for JEE (Advanced) – 2018
The candidates who are declared eligible for JEE (Advanced) – 2018 will have to again register later on at the JEE (Advanced) website http://jeeadv.ac.in after the declaration of the JEE (Main)-2018 score. They may note that it is compulsory to appear in both the papers of JEE (Advanced) – 2018 to be eligible for admission to IIT. For latest information related to JEE (Advanced) kindly visit the JEE (Advanced) website http://jeeadv.ac.in
6. ADMIT CARD FOR JEE (Main) – 2018
The Admit Card can be downloaded from JEE (Main) website from 2ndweek March 2018 onwards. The candidates are advised to download their admit cards from JEE (Main) website only. The Candidates are also advised to regularly see JEE (Main) website for updates. A help desk will also be functional on all working days from 9.00 AM to 5.30 PM for general facilitation. The phone numbers of the help desk are available on the website of JEE (Main).
7. COMPUTER BASED EXAMINATION FOR PAPER-1 (B. E./B. TECH.) OF JEE (Main)–2018
7.1 Guidelines to Candidates
- Please check the Admit Card carefully for your Name, Paper, Date of Birth, Gender, Test Centre Name, City, State Code of Eligibility and Category. In case of any discrepancy, communicate to JEE (Main) Secretariat/CBSE immediately for necessary action.
- The Admit Card is issued provisionally to the candidate subject to his/her satisfying the eligibility conditions.
- Candidates are advised to reach the venue at least 2½ hours before the examination so as to complete the frisking and registration formalities well before the time. Registration desk will be closed 05 minutes prior to the examination.
- The candidate must show, on demand, the Admit Card for admission in the examination room/hall. A candidate who does not possess the Admit Card issued by the Board shall not be permitted for the examination under any circumstances by the Centre Superintendent.
- The candidates claiming the relaxation under PwD category must carry with them the copy PwD certificate in the prescribed format (Appendix 9) issued by the Competent Authority.
- No candidate, under any circumstances, will be allowed to enter the Examination Centre after the commencement of the examination.
- A seat indicating roll number will be allocated to each candidate. Candidate should find out and occupy their allotted seat only. Any candidate found to have changed room or the seat on his/her own other than allotted, his/her candidature shall be cancelled and no plea would be accepted for it.
- The candidate should ensure that the question paper available on the computer is as per his/her choice of medium. In case, the question paper is in medium other than his/her choice, the same may be brought to the notice of the Invigilator concerned.
- No Candidate will be allowed to carry any baggage inside the Examination Centre.JEE Apex Board will not be responsible for any belongings stolen or lost at the premises.
- Candidates are not allowed to carry any textual material, Calculators, Docu Pen, Slide Rules, Log Tables, Electronic Watches with facilities of calculator, printed or written material, bits of papers, mobile phone, pager or any other device, except the Admit Card, identity proof, document as required under point no. 5 of para 7.1 inside the Examination Room/Hall. If any candidate is in possession of any of the above items, his/her candidature will be treated as unfair means and his/her current examination will be cancelled & he/she will also be debarred for future examination(s) & the equipment will be seized.
- Smoking and eating is strictly prohibited in the examination room.
- Tea, coffee, cold drinks or snacks are not allowed to be taken into the examination rooms during examination hours.
- Approach the Centre Superintendent/Invigilator in the room for any technical assistance, first aid emergency or any other information during the course of examination.
- No candidate, without the special permission of the Centre Superintendent or the Invigilator concerned, will leave his/her seat or Examination Room until the full duration of the paper. Candidates must follow the instructions strictly as instructed by the Centre Superintendent/Invigilators.
- For any queries or issues regarding computer based examination, the candidates may contact on toll free Call Centre No. which will be available on JEE (Main) website later on.
- The candidates, suffering from diabetes, are allowed to carry into the examination hall the eatables like sugar tablets / fruits (like banana/apple/ orange) and transparent water bottle. However, the candidates are not allowed to carry packed foods like chocolate / candy/ sandwich in the examination hall.
7.2 Instructions for Computer Based Examination
The Computer Based Examination will be conducted as per the following schedule.
- A sample/mock test will be available on JEE (Main) website in the month of December 2017 for practice purpose and to give the candidate look and feel of the Computer Based Examination (CBE).
- The test will start exactly at the time mentioned in the Admit Card and an announcement to this effect will be made by the invigilator.
- The test will be of 3 hrs duration.
- The test paper will be consisting questions of Physics, Chemistry & Mathematics and all questions will have equal weightage.
- There will be three parts in the question paper consisting of Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics having equal weightage.
- Each question is allotted 4 (four) marks for the correct response. ¼ (one fourth) marks i.e. one mark will be deducted for indicating incorrect response of each question. No deduction from the total score will be made if no response is indicated for a question.
- There is only one correct response for each question out of four responses given.
- The Ball Pens will be supplied to the candidates in the examination hall so they should not bring any type of Pen/Ball Pens with them.
- All calculations/writing work are to be done only in the rough sheet provided at the centre and on completion of the test candidates must hand over the rough sheets to the invigilator on duty in the Room/Hall.
- During the examination time, the invigilator will check Admit Card of the candidate to satisfy himself/herself about the identity of each candidate.
- The candidates are governed by all Rules and Regulations of the Board with regard to their conduct in the Examination Hall. All cases of unfair means will be dealt with as per rules.
- The candidates must sign on the Attendance Sheet at the appropriate place.
8. PEN AND PAPER BASED EXAMINATION FOR PAPER-1 (B. E./B. TECH.) AND PAPER-2 (B. ARCH./B. PLANNING.) OF JEE (Main) – 2018
8.1 Guidelines to Candidates
- Please check the Admit Card carefully for your Name, Paper, Date of Birth, Gender, Test Centre Name, City, State Code of Eligibility and Category. In case of any discrepancy, communicate to JEE (Main) Secretariat/CBSE immediately for necessary action.
- The Admit Card is issued provisionally to the candidate subject to his/her satisfying the eligibility conditions.
- The examination rooms/hall will be opened 2½ hours before the commencement of the test. Since the Candidates will be frisked by metal detector so they should report at 7.00 a.m. at examination centre to avoid rush at the time of frisking. The candidates should take their seats in the examination hall immediately after frisking. If the candidates do not report in time, they are likely to miss some of the general instructions to be announced in the Examination Hall.
- The candidate must show, on demand, the Admit Card for admission in the examination room/hall. A candidate who does not possess the Admit Card issued by the Board shall not be permitted for the examination under any circumstances by the Centre Superintendent.
- For Aptitude Test in Architecture, candidates are advised to bring their own geometry box set, pencils, erasers and colour pencils or crayons.
- Candidates are advised to bring with them a cardboard or a clip board on which nothing should be written, so that they have no difficulty in filling responses in the Answer Sheet even if the tables provided in the examination room/hall do have smooth surface.
- The candidates claiming the relaxation under PwD category must carry with them the copy PwD certificate in the prescribed format (Appendix 9) issued by the Competent Authority.
- No candidate, under any circumstances, will be allowed to enter the Examination Centre after the commencement of the examination.
- A seat indicating roll number will be allocated to each candidate. Candidate should find out and occupy their allotted seat only. Any candidate found to have changed room or the seat on his/her own other than allotted, his/her candidature shall be cancelled and no plea would be accepted for it.
- Ten minutes before the commencement of the paper, each candidate will be given sealed Test Booklet with an Answer Sheet placed inside it.
- Immediately on receipt of the Test Booklet the candidate will fill in the required particulars on the cover page of the Test Booklet with Ball Point Pen only. He/She will not open the Test Booklet until asked to do so by the Invigilator. Do not open/break the seal before the announcement.
- Candidates must follow the instructions strictly as instructed by the Centre Superintendent/Invigilators.
- No Candidate will be allowed to carry any baggage inside the Examination Centre. JEE Apex Board will not be responsible for any belongings stolen or lost at the premises.
- Candidates are not allowed to carry any textual material, Calculators, Docu Pen, Slide Rules, Log Tables, Electronic Watches with facilities of calculator, printed or written material, bits of papers, mobile phone, pager or any other device, except the Admit Card, identity proof, document as required under point no. 7 inside the Examination Room/Hall. If any candidate is in possession of any of the above items, his/her candidature will be treated as unfairmeans and his/her current examination will be cancelled & he/she will also be debarred for future examination(s) & the equipment will be seized.
- Smoking and eating is strictly prohibited in the examination room.
- Tea, coffee, cold drinks or snacks are not allowed to be taken into the examination rooms during examination hours.
- No candidate, without the special permission of the Centre Superintendent or the Invigilator concerned, will leave his/her seat or Examination Room until the full duration of the paper. Candidates should not leave the room/hall without handing over their Answer Sheets to the Invigilators on duty.
- The candidates, suffering from diabetes, are allowed to carry into the examination hall the eatables like sugar tablets / fruits (like banana/apple/ orange) and transparent water bottle. However, the candidates are not allowed to carry packed foods like chocolate / candy/ sandwich in the examination hall.
8.2 Instructions for Pen and Paper Based Examination
- Five minutes before the commencement of the paper the candidate will be asked to break/open the seal of the Test Booklet. He/She will take out the Answer Sheet carefully. The candidate should check carefully that the Test Booklet Code printed on Side-2 of the Answer Sheet is the same as printed on the Test Booklet. In case of discrepancy, the candidate should immediately report the matter to the Invigilator for replacement of both the Test Booklet and the Answer Sheet.
- Candidate will then write particulars with Blue/Black ball point pen only on both the sides of the Answer Sheet. Use of pencil is strictly prohibited. If one uses the pencil, his/her answer sheet will be rejected and no correspondence will be entertained in this regard. After completing this step, the candidates will wait for the instruction by the invigilator.
- The test will start exactly at the time mentioned in the Admit Card and an announcement to this effect will be made by the invigilator.
- The test will be of 3 hrs duration.
- The test paper will be consisting questions of Physics, Chemistry & Mathematics and all questions will have equal weightage.
- There will be three parts in the question paper consisting of Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics having equal weightage.
- Each question is allotted 4 (four) marks for the correct response. ¼ (one fourth) marks i.e. one mark will be deducted for indicating incorrect response of each question. No deduction from the total score will be made if no response is indicated for a question.
- There is only one correct response for each question out of four responses given. In case, the candidate darkens more than one response for a question, one mark will be deducted.
- During the examination time, the invigilator will check Admit Card of the candidate to satisfy himself/herself about the identity of each candidate. The invigilator will also put his/her signatures in the place provided in the Answer Sheet on Side-1.
- The Ball Pens will be supplied to the candidates in the examination hall so they should not bring any type of Pen/Ball Pens with them.
- A signal will be given at the beginning of the examination and at half-time. A signal will also be given before the closing time when the candidate must stop marking the responses.
- The candidate will check that the Test-booklet contains as many numbers of pages as are written on the top of the first page of the Test Booklet. The candidates should also verify the serial number and series of the Test Booklet with the serial number and series of OMR sheet. In case of any variation, the Test Booklet and OMR sheet should be immediately returned to the invigilator for the replacement with another set of same series available in the examination hall/centre.
- The candidates must sign twice on the Attendance Sheet at the appropriate place. Firstly, immediately after commencement of the Examination and for the second time while handing over the Answer Sheet to the Invigilator. The candidates are also required to put their left hand thumb impression in the space provided in the Attendance Sheet.
- The candidates are governed by all Rules and Regulations of the Board with regard to their conduct in the Examination Hall. All cases of unfair means will be dealt with as per rules.
9. CODE OF CONDUCT FOR CANDIDATES DURING JEE (Main) – 2018
Candidates shall maintain perfect silence and attend to their Question Paper only. Any conversation or gesture or disturbance in the Examination Room/Hall shall be deemed as misbehaviour. If a candidate is found using unfair means or impersonating, his/her candidature shall be cancelled and he/she will be liable to be debarred for taking examination either permanently or for a specified period according to the nature of offence.
Candidates are not allowed to carry any textual material, Calculators, Docu Pen, Slide Rules, Log Tables, Electronic Watches with facilities of calculator, printed or written material, bits of papers, mobile phone, pager or any other device, except the Admit Card inside the Examination Room/Hall. If any candidate is in possession of any of the above item, his/her candidature will be treated as unfairmeans and his/her current examination will be cancelled & he/she will also be debarred for future examination(s) & the equipment will be seized.
The candidate shall not remove any page(s) from the Test-Booklet (in case of Pen and Paper Based Examination) and if he/she is found to have removed any page(s) from his/her Test Booklet, he/she will be presumed to have used unfair means and shall be liable for criminal action.
Appendix 1
Mathematics Syllabus For JEE (Main) – 2018
UNIT 1: Sets, Relations and Functions
Sets and their representation; Union, intersection and complement of sets and their algebraic properties; Power set; Relation, Types of relations, equivalence relations, functions;. one-one, into and onto functions, composition of functions.
UNIT 2: Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations
Complex numbers as ordered pairs of reals, Representation of complex numbers in the form a+ib and their representation in a plane, Argand diagram, algebra of complex numbers, modulus and argument (or amplitude) of a complex number, square root of a complex number, triangle inequality, Quadratic equations in real and complex number system and their solutions. Relation between roots and co-efficients, nature of roots, formation of quadratic equations with given roots.
UNIT 3: Matrices and Determinants
Matrices, algebra of matrices, types of matrices, determinants and matrices of order two and three. Properties of determinants, evaluation of determinants, area of triangles using determinants. Adjoint and evaluation of inverse of a square matrix using determinants and elementary transformations, Test of consistency and solution of simultaneous linear equations in two or three variables using determinants and matrices.
UNIT 4: Permutations and Combinations
Fundamental principle of counting, permutation as an arrangement and combination as selection, Meaning of P (n,r) and C (n,r), simple applications.
UNIT 5: Mathematical Induction
Principle of Mathematical Induction and its simple applications.
UNIT 6: Binomial Theorem
Binomial theorem for a positive integral index, general term and middle term, properties of Binomial coefficients and simple applications.
UNIT 7: Sequences and Series
Arithmetic and Geometric progressions, insertion of arithmetic, geometric means between two given numbers. Relation between A.M. and G.M. Sum upto n terms of special series: Sn, Sn2, Sn3. Arithmetico – Geometric progression.
UNIT 8: Limit, Continuity and Differentiability
Real – valued functions, algebra of functions, polynomials, rational, trigonometric, logarithmic and exponential functions, inverse functions. Graphs of simple functions. Limits, continuity and differentiability. Differentiation of the sum, difference, product and quotient of two functions. Differentiation of trigonometric, inverse trigonometric, logarithmic, exponential, composite and implicit functions; derivatives of order upto two. Rolle’s and Lagrange’s Mean Value Theorems. Applications of derivatives: Rate of change of quantities, monotonic – increasing and decreasing functions, Maxima and minima of functions of one variable, tangents and normals.
UNIT 9: Integral Calculus
Integral as an anti – derivative. Fundamental integrals involving algebraic, trigonometric, exponential and logarithmic functions. Integration by substitution, by parts and by partial fractions. Integration using trigonometric identities.
Evaluation of simple integrals of the type
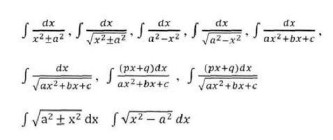
Integral as limit of a sum. Fundamental Theorem of Calculus. Properties of definite integrals. Evaluation of definite integrals, determining areas of the regions bounded by simple curves in standard form.
UNIT 10: Differential Equations
Ordinary differential equations, their order and degree. Formation of differential equations. Solution of differential equations by the method of separation of variables, solution of homogeneous and linear differential equations of the type:
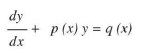
UNIT 11: Co-ordinate Geometry
Cartesian system of rectangular co-ordinates in a plane, distance formula, section formula, locus and its equation, translation of axes, slope of a line, parallel and perpendicular lines, intercepts of a line on the coordinate axes.
Straight lines
Various forms of equations of a line, intersection of lines, angles between two lines, conditions for concurrence of three lines, distance of a point from a line, equations of internal and external bisectors of angles between two lines, coordinates of centroid, orthocentre and circumcentre of a triangle, equation of family of lines passing through the point of intersection of two lines.
Circles, conic sections
Standard form of equation of a circle, general form of the equation of a circle, its radius and centre, equation of a circle when the end points of a diameter are given, points of intersection of a line and a circle with the centre at the origin and condition for a line to be tangent to a circle, equation of the tangent. Sections of cones, equations of conic sections (parabola, ellipse and hyperbola) in standard forms, condition for y = mx + c to be a tangent and point (s) of tangency.
UNIT 12: Three Dimensional Geometry
Coordinates of a point in space, distance between two points, section formula, direction ratios and direction cosines, angle between two intersecting lines. Skew lines, the shortest distance between them and its equation. Equations of a line and a plane in different forms, intersection of a line and a plane, coplanar lines.
UNIT 13: Vector Algebra
Vectors and scalars, addition of vectors, components of a vector in two dimensions and three dimensional space, scalar and vector products, scalar and vector triple product.
UNIT 14: Statistics and Probability
Measures of Dispersion
Calculation of mean, median, mode of grouped and ungrouped data. Calculation of standard deviation, variance and mean deviation for grouped and ungrouped data.
Probability
Probability of an event, addition and multiplication theorems of probability, Baye’s theorem, probability distribution of a random variate, Bernoulli trials and Binomial distribution.
UNIT 15: Trigonometry
Trigonometrical identities and equations. Trigonometrical functions. Inverse trigonometrical functions and their properties. Heights and Distances.
UNIT 16: Mathematical Reasoning
Statements, logical operations and, or, implies, implied by, if and only if. Understanding of tautology, contradiction, converse and contrapositive.
Physics Syllabus For JEE (Main) – 2018
The syllabus contains two Sections – A and B. Section – A pertains to the Theory Part having 80% weightage, while Section – B contains Practical Component (Experimental Skills) having 20% weightage.
SECTION A
UNIT 1: Physics and Measurement
Physics, technology and society, S I units, Fundamental and derived units. Least count, accuracy and precision of measuring instruments, Errors in measurement, Significant figures. Dimensions of Physical quantities, dimensional analysis and its applications.
UNIT 2: Kinematics
Frame of reference. Motion in a straight line: Position-time graph, speed and velocity. Uniform and non-uniform motion, average speed and instantaneous velocity Uniformly accelerated motion, velocity-time, position- time graphs, relations for uniformly accelerated motion. Scalars and Vectors, Vector addition and Subtraction, Zero Vector, Scalar and Vector products, Unit Vector, Resolution of a Vector. Relative Velocity, Motion in a plane, Projectile Motion, Uniform Circular Motion.
UNIT 3: Laws of Motion
Force and Inertia, Newton’s First Law of motion; Momentum, Newton’s Second Law of motion; Impulse; Newton’s Third Law of motion. Law of conservation of linear momentum and its applications, Equilibrium of concurrent forces.
Static and Kinetic friction, laws of friction, rolling friction.
Dynamics of uniform circular motion: Centripetal force and its applications.
UNIT 4: Work, Energy and Power
Work done by a constant force and a variable force; kinetic and potential energies, work energy theorem, power.
Potential energy of a spring, conservation of mechanical energy, conservative and non-conservative forces; Elastic and inelastic collisions in one and two dimensions.
UNIT 5: Rotational Motion
Centre of mass of a two-particle system, Centre of mass of a rigid body; Basic concepts of rotational motion; moment of a force, torque, angular momentum, conservation of angular momentum and its applications; moment of inertia, radius of gyration. Values of moments of inertia for simple geometrical objects, parallel and perpendicular axes theorems and their applications. Rigid body rotation, equations of rotational motion.
UNIT 6: Gravitation
The universal law of gravitation. Acceleration due to gravity and its variation with altitude and depth. Kepler’s laws of planetary motion. Gravitational potential energy; gravitational potential. Escape velocity. Orbital velocity of a satellite. Geo-stationary satellites.
UNIT 7: Properties of Solids and Liquids
Elastic behaviour, Stress-strain relationship, Hooke’s Law, Young’s modulus, bulk modulus, modulus of rigidity. Pressure due to a fluid column; Pascal’s law and its applications. Viscosity, Stokes’ law, terminal velocity, streamline and turbulent flow, Reynolds number. Bernoulli’s principle and its applications. Surface energy and surface tension, angle of contact, application of surface tension – drops, bubbles and capillary rise. Heat, temperature, thermal expansion; specific heat capacity, calorimetry; change of state, latent heat. Heat transfer- conduction, convection and radiation, Newton’s law of cooling.
UNIT 8: Thermodynamics
Thermal equilibrium, zeroth law of thermodynamics, concept of temperature. Heat, work and internal energy. First law of thermodynamics. Second law of thermodynamics: reversible and irreversible processes. Carnot engine and its efficiency.
UNIT 9: Kinetic Theory of Gases
Equation of state of a perfect gas, work doneon compressing a gas.Kinetic theory of gases – assumptions, concept of pressure. Kinetic energy and temperature: rms speed of gas molecules; Degrees of freedom, Law of equipartition of energy,applications to specific heat capacities of gases; Mean free path, Avogadro’s number.
UNIT 10: Oscillations and Waves
Periodic motion – period, frequency, displacement as a function of time. Periodic functions. Simple harmonic motion (S.H.M.) and its equation; phase; oscillations of a spring -restoring force and force constant; energy in S.H.M. – kinetic and potential energies; Simple pendulum – derivation of expression for its time period; Free, forced and damped oscillations, resonance.
Wave motion. Longitudinal and transverse waves, speed of a wave. Displacement relation for a progressive wave. Principle of superposition of waves, reflection of waves, Standing waves in strings and organ pipes, fundamental mode and harmonics, Beats, Doppler effect in sound
UNIT 11: Electrostatics
Electric charges: Conservation of charge, Coulomb’s law-forces between two point charges, forces between multiple charges; superposition principle and continuous charge distribution.
Electric field: Electric field due to a point charge, Electric field lines, Electric dipole, Electric field due to a dipole, Torque on a dipole in a uniform electric field.
Electric flux, Gauss’s law and its applications to find field due to infinitely long uniformly charged straight wire, uniformly charged infinite plane sheet and uniformly charged thin spherical shell. Electric potential and its calculation for a point charge, electric dipole and system of charges; Equipotential surfaces, Electrical potential energy of a system of two point charges in an electrostatic field.
Conductors and insulators, Dielectrics and electric polarization, capacitor, combination of capacitors in series and in parallel, capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor with and without dielectric medium between the plates, Energy stored in a capacitor.
UNIT 12: Current Electricity
Electric current, Drift velocity, Ohm’s law, Electrical resistance, Resistances of different materials, V-I characteristics of Ohmic and nonohmic conductors, Electrical energy and power, Electrical resistivity, Colour code for resistors; Series and parallel combinations of resistors; Temperature dependence of resistance.
Electric Cell and its Internal resistance, potential difference and emf of a cell, combination of cells in series and in parallel. Kirchhoff’s laws and their applications. Wheatstone bridge, Metre bridge. Potentiometer – principle and its applications.
UNIT 13: Magnetic Effects of Current and Magnetism
Biot – Savart law and its application to current carrying circular loop. Ampere’s law and its applications to infinitely long current carrying straight wire and solenoid. Force on a moving charge in uniform magnetic and electric fields. Cyclotron.
Force on a current-carrying conductor in a uniform magnetic field. Force between two parallel current-carrying conductors-definition of ampere. Torque experienced by a current loop in uniform magnetic field; Moving coil galvanometer, its current sensitivity and conversion to ammeter and voltmeter.
Current loop as a magnetic dipole and its magnetic dipole moment. Bar magnet as an equivalent solenoid, magnetic field lines; Earth’s magnetic field and magnetic elements. Para-, dia- and ferro- magnetic substances.
Magnetic susceptibility and permeability, Hysteresis, Electromagnets and permanent magnets.
UNIT 14: Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents
Electromagnetic induction; Faraday’s law, induced emf and current; Lenz’s Law, Eddy currents. Self and mutual inductance. Alternating currents, peak and rms value of alternating current/ voltage; reactance and impedance; LCR series circuit, resonance; Quality factor, power in AC circuits, wattless current. AC generator and transformer.
UNIT 15: Electromagnetic Waves
Electromagnetic waves and their characteristics. Transverse nature of electromagnetic waves.
Electromagnetic spectrum (radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible, ultraviolet, Xrays, gamma rays). Applications of e.m. waves.
UNIT 16: Optics
Reflection and refraction of light at plane and spherical surfaces, mirror formula, Total internal reflection and its applications, Deviation and Dispersion of light by a prism, Lens Formula, Magnification, Power of a Lens, Combination of thin lenses in contact, Microscope and Astronomical Telescope (reflecting and refracting) and their magnifying powers.
Wave optics: wavefront and Huygens’ principle, Laws of reflection and refraction using Huygen’s principle. Interference, Young’s double slit experiment and expression for fringe width, coherent sources and sustained interference of light. Diffraction due to a single slit, width of central maximum. Resolving power of microscopes and astronomical telescopes, Polarisation, plane polarized light; Brewster’s law, uses of plane polarized light and Polaroids.
UNIT 17: Dual Nature of Matter and Radiation
Dual nature of radiation. Photoelectric effect, Hertz and Lenard’s observations; Einstein’s photoelectric equation; particle nature of light. Matter waves-wave nature of particle, de Broglie relation. Davisson-Germer experiment.
UNIT 18: Atoms and Nuclei
Alpha-particle scattering experiment; Rutherford’s model of atom; Bohr model, energy levels, hydrogen spectrum. Composition and size of nucleus, atomic masses, isotopes, isobars; isotones. Radioactivity-alpha, beta and gamma particles/rays and their properties; radioactive decay law. Mass-energy relation, mass defect; binding energy per nucleon and its variation with mass number, nuclear fission and fusion.
UNIT 19: Electronic Devices
Semiconductors; semiconductor diode: I-V characteristics in forward and reverse bias; diode as a rectifier; I-V characteristics of LED, photodiode, solar cell and Zener diode; Zener diode as a voltage regulator. Junction transistor, transistor action, characteristics of a transistor; transistor as an amplifier (common emitter configuration) and oscillator. Logic gates (OR, AND, NOT, NAND and NOR). Transistor as a switch.
UNIT 20: Communication Systems
Propagation of electromagnetic waves in the atmosphere; Sky and space wave propagation, Need for modulation, Amplitude and Frequency Modulation, Bandwidth of signals, Bandwidth of Transmission medium, Basic Elements of a Communication System (Block Diagram only)
SECTION-B
UNIT 21: Experimental Skills
Familiarity with the basic approach and observations of the experiments and activities:
- Vernier callipers – its use to measure internal and external diameter and depth of a vessel.
- Screw gauge-its use to determine thickness/diameter of thin sheet/wire.
- Simple Pendulum-dissipation of energy by plotting a graph between square of amplitude and time.
- Metre Scale – mass of a given object by principle of moments.
- Young’s modulus of elasticity of the material of a metallic wire.
- Surface tension of water by capillary rise and effect of detergents.
- Co-efficient of Viscosity of a given viscous liquid by measuring terminal velocity of a given spherical body.
- Plotting a cooling curve for the relationship between the temperature of a hot body and time.
- Speed of sound in air at room temperature using a resonance tube.
- Specific heat capacity of a given (i) solid and (ii) liquid by method of mixtures.
- Resistivity of the material of a given wire using metre bridge.
- Resistance of a given wire using Ohm’s law.
- Potentiometer – (i) Comparison of emf of two primary cells. (ii) Determination of internal resistance of a cell.
- Resistance and figure of merit of a galvanometer by half deflection method.
- Focal length of: (i) Convex mirror (ii) Concave mirror, and (iii) Convex lens using parallax method.
- Plot of angle of deviation vs angle of incidence for a triangular prism.
- Refractive index of a glass slab using a travelling microscope.
- Characteristic curves of a p-n junction diode in forward and reverse bias.
- Characteristic curves of a Zener diode and finding reverse break down voltage.
- Characteristic curves of a transistor and finding current gain and voltage gain.
- Identification of Diode, LED, Transistor, IC, Resistor, Capacitor from mixed collection of such items.
- Using multimeter to: (i) Identify base of a transistor (ii) Distinguish between npn and pnp type transistor (iii) See the unidirectional flow of current in case of a diode and an LED. (iv) Check the correctness or otherwise of a given electronic component (diode, transistor or IC).
Chemistry Syllabus For JEE (Main) – 2018
Section A: Physical Chemistry
UNIT 1: Some Basic concepts in Chemistry
Matter and its nature, Dalton’s atomic theory; Concept of atom, molecule, element and compound; Physical quantities and their measurements in Chemistry, precision and accuracy, significant figures, S.I. Units, dimensional analysis; Laws of chemical combination; Atomic and molecular masses, mole concept, molar mass, percentage composition, empirical and molecular formulae; Chemical equations and stoichiometry.
UNIT 2: States of Matter
Classification of matter into solid, liquid and gaseous states.
Gaseous State:
Measurable properties of gases; Gas laws – Boyle’s law, Charle’s law, Graham’s law of diffusion, Avogadro’s law, Dalton’s law of partial pressure; Concept of Absolute scale of temperature; Ideal gas equation, Kinetic theory of gases (only postulates); Concept of average, root mean square and most probable velocities; Real gases, deviation from Ideal behaviour, compressibility factor, van der Waals equation, liquefaction of gases, critical constants.
Liquid State:
Properties of liquids – vapour pressure, viscosity and surface tension and effect of temperature on them (qualitative treatment only).
Solid State:
Classification of solids: molecular, ionic, covalent and metallic solids, amorphous and crystalline solids (elementary idea); Bragg’s Law and its applications; Unit cell and lattices, packing in solids (fcc, bcc and hcp lattices), voids, calculations involving unit cell parameters, imperfection in solids; Electrical, magnetic and dielectric properties.
UNIT 3: Atomic Structure
Discovery of sub-atomic particles (electron, proton and neutron); Thomson and Rutherford atomic models and their limitations; Nature of electromagnetic radiation, photoelectric effect; Spectrum of hydrogen atom, Bohr model of hydrogen atom – its postulates, derivation of the relations for energy of the electron and radii of the different orbits, limitations of Bohr’s model; Dual nature of matter, de-Broglie’s relationship, Heisenberg uncertainty principle.
Elementary ideas of quantum mechanics, quantum mechanical model of atom, its important features, concept of atomic orbitals as one electron wave functions; Variation of Ψ and Ψ2 with r for 1s and 2s orbitals; various quantum numbers (principal, angular momentum and magnetic quantum numbers) and their significance; shapes of s, p and d – orbitals, electron spin and spin quantum number; Rules for filling electrons in orbitals – aufbau principle, Pauli’s exclusion principle and Hund’s rule, electronic configuration of elements, extra stability of half-filled and completely filled orbitals.
UNIT 4: Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
Kossel – Lewis approach to chemical bond formation, concept of ionic and covalent bonds.
Ionic Bonding: Formation of ionic bonds, factors affecting the formation of ionic bonds; calculation of lattice enthalpy.
Covalent Bonding: Concept of electronegativity, Fajan’s rule, dipole moment; Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) theory and shapes of simple molecules.
Quantum mechanical approach to covalent bonding: Valence bond theory – Its important features, concept of hybridization involving s, p and d orbitals; Resonance.
Molecular Orbital Theory – Its important features, LCAOs, types of molecular orbitals (bonding, antibonding), sigma and pi-bonds, molecular orbital electronic configurations of homonuclear diatomic molecules, concept of bond order, bond length and bond energy.
Elementary idea of metallic bonding. Hydrogen bonding and its applications.
UNIT 5: Chemical Thermodynamics
Fundamentals of thermodynamics: System and surroundings, extensive and intensive properties, state functions, types of processes.
First law of thermodynamics: Concept of work, heat internal energy and enthalpy, heat capacity, molar heat capacity; Hess’s law of constant heat summation; Enthalpies of bond dissociation, combustion, formation, atomization, sublimation, phase transition, hydration, ionization and solution.
Second law of thermodynamics: Spontaneity of processes; ΔS of the universe and ΔG of the system as criteria for spontaneity, ΔGo (Standard Gibbs energy change) and equilibrium constant.
UNIT 6: Solutions
Different methods for expressing concentration of solution – molality, molarity, mole fraction, percentage (by volume and mass both), vapour pressure of solutions and Raoult’s Law – Ideal and non-ideal solutions, vapour pressure – composition, plots for ideal and non-ideal solutions; Colligative properties of dilute solutions – relative lowering of vapour pressure, depression of freezing point, elevation of boiling point and osmotic pressure; Determination of molecular mass using colligative properties; Abnormal value of molar mass, van’t Hoff factor and its significance.
UNIT 7: Equilibrium
Meaning of equilibrium, concept of dynamic equilibrium.
Equilibria involving physical processes: Solid -liquid, liquid – gas and solid – gas equilibria, Henry’s law, general characterics of equilibrium involving physical processes.
Equilibria involving chemical processes: Law of chemical equilibrium, equilibrium constants (Kp and Kc) and their significance, significance of ΔG and ΔGo in chemical equilibria, factors affecting equilibrium concentration, pressure, temperature, effect of catalyst; Le Chatelier’s principle.
Ionic equilibrium: Weak and strong electrolytes, ionization of electrolytes, various concepts of acids and bases (Arrhenius, Bronsted – Lowry and Lewis) and their ionization, acid – base equilibria (including multistage ionization) and ionization constants, ionization of water, pH scale, common ion effect, hydrolysis of salts and pH of their solutions, solubility of sparingly soluble salts and solubility products, buffer solutions.
UNIT 8: Redox Reactions and Electrochemistry
Electronic concepts of oxidation and reduction, redox reactions, oxidation number, rules for assigning oxidation number, balancing of redox reactions.
Eectrolytic and metallic conduction, conductance in electrolytic solutions, specific and molar conductivities and their variation with concentration: Kohlrausch’s law and its applications.
Electrochemical cells – Electrolytic and Galvanic cells, different types of electrodes, electrode potentials including standard electrode potential, half – cell and cell reactions, emf of a Galvanic cell and its measurement; Nernst equation and its applications; Relationship between cell potential and Gibbs’ energy change; Dry cell and lead accumulator; Fuel cells; Corrosion and its prevention.
UNIT 9: Chemical Kinetics
Rate of a chemical reaction, factors affecting the rate of reactions: concentration, temperature, pressure and catalyst; elementary and complex reactions, order and molecularity of reactions, rate law, rate constant and its units, differential and integral forms of zero and first order reactions, their characteristics and half – lives, effect of temperature on rate of reactions – Arrhenius theory, activation energy and its calculation, collision theory of bimolecular gaseous reactions (no derivation).
UNIT 10: Surface Chemistry
Adsorption – Physisorption and chemisorption and their characteristics, factors affecting adsorption of gases on solids – Freundlich and Langmuir adsorption isotherms, adsorption from solutions.
Catalysis – Homogeneous and heterogeneous, activity and selectivity of solid catalysts, enzyme catalysis and its mechanism.
Colloidal state – distinction among true solutions, colloids and suspensions, classification of colloids – lyophilic, lyophobic; multi molecular, macromolecular and associated colloids (micelles), preparation and properties of colloids – Tyndall effect, Brownian movement, electrophoresis, dialysis, coagulation and flocculation; Emulsions and their characteristics.
Section B: Inorganic Chemistry
UNIT 11: Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties
Modem periodic law and present form of the periodic table, s, p, d and f block elements, periodic trends in properties of elementsatomic and ionic radii, ionization enthalpy, electron gain enthalpy, valence, oxidation states and chemical reactivity.
UNIT 12: General Principles and Process of Isolation of Metals
Modes of occurrence of elements in nature, minerals, ores; steps involved in the extraction of metals – concentration, reduction (chemical. and electrolytic methods) and refining with special reference to the extraction of Al, Cu, Zn and Fe; Thermodynamic and electrochemical principles involved in the extraction of metals.
UNIT 13: Hydrogen
Position of hydrogen in periodic table, isotopes, preparation, properties and uses of hydrogen; Physical and chemical properties of water and heavy water; Structure, preparation, reactions and uses of hydrogen peroxide; Classification of hydrides – ionic, covalent and interstitial; Hydrogen as a fuel.
UNIT 14: s – Block Elements (Alkali and Alkaline Earth Metals)
Group 1 and Group 2 Elements
General introduction, electronic configuration and general trends in physical and chemical properties of elements, anomalous properties of the first element of each group, diagonal relationships.
Preparation and properties of some important compounds – sodium carbonate, sodium chloride, sodium hydroxide and sodium hydrogen carbonate; Industrial uses of lime, limestone, Plaster of Paris and cement; Biological significance of Na, K, Mg and Ca.
UNIT 15: p – Block Elements
Group 13 to Group 18 Elements
General Introduction: Electronic configuration and general trends in physical and chemical properties of elements across the periods and down the groups; unique behaviour of the first element in each group.
Groupwise study of the p – block elements
Group – 13
Preparation, properties and uses of boron and aluminium; Structure, properties and uses of borax, boric acid, diborane, boron trifluoride, aluminium chloride and alums.
Group – 14
Tendency for catenation; Structure, properties and uses of allotropes and oxides of carbon, silicon tetrachloride, silicates, zeolites and silicones.
Group – 15
Properties and uses of nitrogen and phosphorus; Allotrophic forms of phosphorus; Preparation, properties, structure and uses of ammonia, nitric acid, phosphine and phosphorus halides, (PCl3, PCl5); Structures of oxides and oxoacids of nitrogen and phosphorus.
Group – 16
Preparation, properties, structures and uses of dioxygen and ozone; Allotropic forms of sulphur; Preparation, properties, structures and uses of sulphur dioxide, sulphuric acid (including its industrial preparation); Structures of oxoacids of sulphur.
Group – 17
Preparation, properties and uses of chlorine and hydrochloric acid; Trends in the acidic nature of hydrogen halides; Structures of Interhalogen compounds and oxides and oxoacids of halogens.
Group – 18
Occurrence and uses of noble gases; Structures of fluorides and oxides of xenon.
UNIT 16: d – and f – Block Elements
Transition Elements
General introduction, electronic configuration, occurrence and characteristics, general trends in properties of the first row transition elements – physical properties, ionization enthalpy, oxidation states, atomic radii, colour, catalytic behaviour, magnetic properties, complex formation, interstitial compounds, alloy formation; Preparation, properties and uses of K2Cr2O7 and KMnO4.
Inner Transition Elements
Lanthanoids – Electronic configuration, oxidation states, chemical reactivity and lanthanoid contraction.
Actinoids – Electronic configuration and oxidation states.
UNIT 17: Co-ordination Compounds
Introduction to co-ordination compounds, Werner’s theory; ligands, co-ordination number, denticity, chelation; IUPAC nomenclature of mononuclear co-ordination compounds, isomerism; Bonding-Valence bond approach and basic ideas of Crystal field theory, colour and magnetic properties; Importance of co-ordination compounds (in qualitative analysis, extraction of metals and in biological systems).
UNIT 18: Environmental Chemistry
Environmental pollution – Atmospheric, water and soil.
Atmospheric pollution – Tropospheric and stratospheric
Tropospheric pollutants – Gaseous pollutants: Oxides of carbon, nitrogen and sulphur, hydrocarbons; their sources, harmful effects and prevention; Green house effect and Global warming; Acid rain; Particulate pollutants: Smoke, dust, smog, fumes, mist; their sources, harmful effects and prevention.
Stratospheric pollution – Formation and breakdown of ozone, depletion of ozone layer – its mechanism and effects.
Water Pollution – Major pollutants such as, pathogens, organic wastes and chemical pollutants; their harmful effects and prevention.
Soil pollution – Major pollutants such as: Pesticides (insecticides,. herbicides and fungicides), their harmful effects and prevention.
Strategies to control environmental pollution.
Section-C: Organic Chemistry
UNIT 19: Purification and Characterisation of Organic Compounds
Purification – Crystallization, sublimation, distillation, differential extraction and chromatography – principles and their applications.
Qualitative analysis – Detection of nitrogen, sulphur, phosphorus and halogens.
Quantitative analysis (basic principles only) – Estimation of carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, halogens, sulphur, phosphorus.
Calculations of empirical formulae and molecular formulae; Numerical problems in organic quantitative analysis.
UNIT 20: Some Basic Principles of Organic Chemistry
Tetravalency of carbon; Shapes of simple molecules – hybridization (s and p); Classification of organic compounds based on functional groups: – C = C – , – C ? C – and those containing halogens, oxygen, nitrogen and sulphur; Homologous series; Isomerism – structural and stereoisomerism.
Nomenclature (Trivial and IUPAC)
Covalent bond fission – Homolytic and heterolytic: free radicals, carbocations and carbanions; stability of carbocations and free radicals, electrophiles and nucleophiles.
Electronic displacement in a covalent bond – Inductive effect, electromeric effect, resonance and hyperconjugation.
Common types of organic reactions – Substitution, addition, elimination and rearrangement.
UNIT 21: Hydrocarbons
Classification, isomerism, IUPAC nomenclature, general methods of preparation, properties and reactions.
Alkanes – Conformations: Sawhorse and Newman projections (of ethane); Mechanism of halogenation of alkanes.
Alkenes – Geometrical isomerism; Mechanism of electrophilic addition: addition of hydrogen, halogens, water, hydrogen halides (Markownikoff’s and peroxide effect); Ozonolysis, oxidation, and polymerization.
Alkynes – Acidic character; Addition of hydrogen, halogens, water and hydrogen halides; Polymerization.
Aromatic hydrocarbons – Nomenclature, benzene – structure and aromaticity; Mechanism of electrophilic substitution: halogenation, nitration, Friedel – Craft’s alkylation and acylation, directive influence of functional group in mono-substituted benzene.
UNIT 22: Organic Compounds Containing Halogens
General methods of preparation, properties and reactions; Nature of C-X bond; Mechanisms of substitution reactions.
Uses; Environmental effects of chloroform, iodoform, freons and DDT.
UNIT 23: Organic Compounds Containing Oxygen
General methods of preparation, properties, reactions and uses.
Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
Alcohols: Identification of primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols; mechanism of dehydration.
Phenols: Acidic nature, electrophilic substitution reactions: halogenation, nitration and sulphonation, Reimer – Tiemann reaction.
Ethers: Structure.
Aldehyde and Ketones
Nature of carbonyl group; Nucleophilic addition to >C=O group, relative reactivities of aldehydes and ketones; Important reactions such as – Nucleophilic addition reactions (addition of HCN, NH3 and its derivatives), Grignard reagent; oxidation; reduction (Wolff Kishner and Clemmensen); acidity of α – hydrogen, aldol condensation, Cannizzaro reaction, Haloform reaction; Chemical tests to distinguish between aldehydes and Ketones.
Carboxylic Acids: Acidic strength and factors affecting it.
UNIT 24: Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen
General methods of preparation, properties, reactions and uses.
Amines: Nomenclature, classification, structure, basic character and identification of primary, secondary and tertiary amines and their basic character.
Diazonium Salts: Importance in synthetic organic chemistry.
UNIT 25: Polymers
General introduction and classification of polymers, general methods of polymerization – addition and condensation, copolymerization;
Natural and synthetic rubber and vulcanization; some important polymers with emphasis on their monomers and uses – polythene, nylon, polyester and bakelite.
UNIT 26: Bio Molecules
General introduction and importance of biomolecules.
Carbohydrates – Classification: aldoses and ketoses; monosaccharides (glucose and fructose), constituent monosaccharides of oligosacchorides (sucrose, lactose, maltose) and polysaccharides (starch, cellulose, glycogen).
Proteins – Elementary Idea of amino acids, peptide bond, polypeptides; Proteins: primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary structure (qualitative idea only), denaturation of proteins, enzymes.
Vitamins – Classification and functions.
Nucleic Acids – Chemical constitution of DNA and RNA. Biological functions of nucleic acids.
UNIT 27: Chemistry in Everyday Life
Chemicals in medicines – Analgesics, tranquilizers, antiseptics, disinfectants, antimicrobials, antifertility drugs, antibiotics, antacids, antihistamins – their meaning and common examples.
Chemicals in food – Preservatives, artificial sweetening agents – common examples.
Cleansing agents – Soaps and detergents, cleansing action.
UNIT 28: Principles Related to Practical Chemistry
Detection of extra elements (N,S, halogens) in organic compounds; Detection of the following functional groups: hydroxyl (alcoholic and phenolic), carbonyl (aldehyde and ketone), carboxyl and amino groups in organic compounds.
Chemistry involved in the preparation of the following:
Inorganic compounds: Mohr’s salt, potash alum.
Organic compounds: Acetanilide, p-nitroacetanilide, aniline yellow, iodoform.
Chemistry involved in the titrimetric excercises – Acids bases and the use of indicators, oxalic-acid vs KMnO4, Mohr’s salt vs KMnO4.
Chemical principles involved in the qualitative salt analysis:
Cations – Pb2+ , Cu2+, AI3+, Fe3+, Zn2+, Ni2+, Ca2+, Ba2+, Mg2+, NH4+.
Anions- CO32-, S2-, SO42-, NO3–, NO2–, Cl–, Br–, I–. (Insoluble salts excluded).
Chemical principles involved in the following experiments:
1. Enthalpy of solution of CuSO4
2. Enthalpy of neutralization of strong acid and strong base. .
3. Preparation of lyophilic and lyophobic sols.
4. Kinetic study of reaction of iodide ion with hydrogen peroxide at room temperature.
Aptitude Test B.Arch/ B.Planning Syllabus For JEE (Main) – 2018
Only applicable for B.Arch./B.Planning candidates.
Part I
Awareness of persons, places, Buildings, Materials.) Objects, Texture related to Architecture and build~environment. Visualising three dimensional objects from two dimensional drawings. Visualising. different sides of three dimensional objects. Analytical Reasoning Mental Ability (Visual, Numerical and Verbal).
Part II
Three dimensional – perception: Understanding and appreciation of scale and proportion of objects, building forms and elements, colour texture, harmony and contrast. Design and drawing of geometrical or abstract shapes and patterns in pencil. Transformation of forms both 2 D and 3 D union, subtraction, rotation, development of surfaces and volumes, Generation of Plan, elevations and 3 D views of objects. Creating two dimensional and three dimensional compositions using given shapes and forms.
Sketching of scenes and activities from memory of urbanscape (public space, market, festivals, street scenes, monuments, recreational spaces etc.), landscape (river fronts, jungles. gardens, trees, plants etc.) and rural life.
Note: Candidates are advised to bring pencils, own geometry box set, erasers and colour pencils and crayons for the Aptitude Test.
Appendix 2
| S.No | STATE | CITY | JEE (Offline) 2018 | JEE (Online) 2018 |
| 1 | ANDAMAN AND NICOBAR | PORT BLAIR | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 2 | ANDHRA PRADESH | ANANTAPUR | Computer Based | |
| 3 | ANDHRA PRADESH | BAPATLA | Computer Based | |
| 4 | ANDHRA PRADESH | BHEEMAVARAM | Computer Based | |
| 5 | ANDHRA PRADESH | CHITTOOR | Computer Based | |
| 6 | ANDHRA PRADESH | ELURU | Computer Based | |
| 7 | ANDHRA PRADESH | GUNTUR | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 8 | ANDHRA PRADESH | KADAPA | Computer Based | |
| 9 | ANDHRA PRADESH | KAKINADA | Computer Based | |
| 10 | ANDHRA PRADESH | KURNOOL | Computer Based | |
| 11 | ANDHRA PRADESH | NELLORE | Computer Based | |
| 12 | ANDHRA PRADESH | ONGOLE | Computer Based | |
| 13 | ANDHRA PRADESH | RAJAHMUNDRY | Computer Based | |
| 14 | ANDHRA PRADESH | SRIKAKULAM | Computer Based | |
| 15 | ANDHRA PRADESH | TADEPALLIGUDEM | Computer Based | |
| 16 | ANDHRA PRADESH | TIRUPATI | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 17 | ANDHRA PRADESH | VIJAYAWADA | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 18 | ANDHRA PRADESH | VISAKHAPATNAM | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 19 | ANDHRA PRADESH | VIZIANAGARAM | Computer Based | |
| 20 | ARUNACHAL PRADESH | ITANAGAR | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 21 | ASSAM | DIBRUGARH | Computer Based | |
| 22 | ASSAM | GUWAHATI | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 23 | ASSAM | JORHAT | Computer Based | |
| 24 | ASSAM | SILCHAR | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 25 | ASSAM | TEZPUR | Computer Based | |
| 26 | BIHAR | AURANGABAD (BIHAR) | Computer Based | |
| 27 | BIHAR | BIHARSHARIF | Computer Based | |
| 28 | BIHAR | BHAGALPUR | Computer Based | |
| 29 | BIHAR | DARBHANGA | Computer Based | |
| 30 | BIHAR | GAYA | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 31 | BIHAR | MUZAFFARPUR | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 32 | BIHAR | PATNA | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 33 | BIHAR | PURNEA | Computer Based | |
| 34 | CHANDIGARH | CHANDIGARH | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 35 | CHHATTISGARH | BHILAI/DURG | Computer Based | |
| 36 | CHHATTISGARH | BILASPUR | Computer Based | |
| 37 | CHHATTISGARH | RAIPUR | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 38 | DADRA NAGAR HAVELI | DADRA NAGAR HAVELI | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 39 | DAMAN & DIU | DAMAN & DIU | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 40 | DELHI | DELHI | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 41 | GOA | PANAJI | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 42 | GUJARAT | AHMEDABAD | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 43 | GUJARAT | ANAND | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 44 | GUJARAT | BHAVNAGAR | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 45 | GUJARAT | GANDHINAGAR | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 46 | GUJARAT | GODHRA | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 47 | GUJARAT | JAMNAGAR | Computer Based | |
| 48 | GUJARAT | JUNAGARH | Computer Based | |
| 49 | GUJARAT | PATAN | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 50 | GUJARAT | RAJKOT | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 51 | GUJARAT | SURAT | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 52 | GUJARAT | VADODARA | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 53 | GUJARAT | VALSAD | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 54 | HARYANA | AMBALA | Computer Based | |
| 55 | HARYANA | BAHADURGARH | Computer Based | |
| 56 | HARYANA | FARIDABAD | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 57 | HARYANA | GURUGRAM | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 58 | HARYANA | HISAR | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 59 | HARYANA | KARNAL | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 60 | HARYANA | KURUKSHETRA | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 61 | HARYANA | PANIPAT | Computer Based | |
| 62 | HARYANA | SONEPAT | Computer Based | |
| 63 | HIMACHAL PRADESH | DHARMSHALA | Computer Based | |
| 64 | HIMACHAL PRADESH | HAMIRPUR | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 65 | HIMACHAL PRADESH | PALAMPUR | Computer Based | |
| 66 | HIMACHAL PRADESH | SHIMLA | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 67 | HIMACHAL PRADESH | SOLAN | Computer Based | |
| 68 | JAMMU AND KASHMIR | BARAMULLAH | Computer Based | |
| 69 | JAMMU AND KASHMIR | JAMMU | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 70 | JAMMU AND KASHMIR | SRINAGAR | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 71 | JHARKHAND | BOKARO | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 72 | JHARKHAND | DHANBAD | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 73 | JHARKHAND | JAMSHEDPUR | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 74 | JHARKHAND | RANCHI | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 75 | KARNATAKA | BAGALKOT | Computer Based | |
| 76 | KARNATAKA | BELGAUM | Computer Based | |
| 77 | KARNATAKA | BELLARY | Computer Based | |
| 78 | KARNATAKA | BENGALURU | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 79 | KARNATAKA | BIDAR | Computer Based | |
| 80 | KARNATAKA | DEVANAGERE | Computer Based | |
| 81 | KARNATAKA | DHARWAD | Computer Based | |
| 82 | KARNATAKA | GULBARGA | Computer Based | |
| 83 | KARNATAKA | HASSAN | Computer Based | |
| 84 | KARNATAKA | HUBBALLI(HUBLI) | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 85 | KARNATAKA | KOLAR | Computer Based | |
| 86 | KARNATAKA | MANIPAL | Computer Based | |
| 87 | KARNATAKA | MANGALURU(MANGALORE) | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 88 | KARNATAKA | MYSORE | Computer Based | |
| 89 | KARNATAKA | SHIVAMOGGA(SHIMOGA) | Computer Based | |
| 90 | KARNATAKA | TUMKUR | Computer Based | |
| 91 | KARNATAKA | UDUPI | Computer Based | |
| 92 | KERALA | ALAPPUZHA | Computer Based | |
| 93 | KERALA | ANGAMALY | Computer Based | |
| 94 | KERALA | CHENGANUR | Computer Based | |
| 95 | KERALA | ERNAKULAM/KOCHI | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 96 | KERALA | IDUKKI | Computer Based | |
| 97 | KERALA | KANJIRAPPALLY | Computer Based | |
| 98 | KERALA | KANNUR | Computer Based | |
| 99 | KERALA | KASARAGOD | Computer Based | |
| 100 | KERALA | KOLLAM | Computer Based | |
| 101 | KERALA | KOTHAMANGALAM | Computer Based | |
| 102 | KERALA | KOTTAYAM | Computer Based | |
| 103 | KERALA | KOZHIKODE | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 104 | KERALA | MALAPURAM | Computer Based | |
| 105 | KERALA | MOOVATTUPUZHA | Computer Based | |
| 106 | KERALA | PALAKKAD | Computer Based | |
| 107 | KERALA | PATHANAMATHITHA | Computer Based | |
| 108 | KERALA | THRISSUR | Computer Based | |
| 109 | KERALA | THIRUVANANTHAPURAM | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 110 | LAKSHADWEEP | KAVARRATI | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 111 | MADHYA PRADESH | BALAGHAT | Computer Based | |
| 112 | MADHYA PRADESH | BETUL | Computer Based | |
| 113 | MADHYA PRADESH | BHOPAL | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 114 | MADHYA PRADESH | CHHATARPUR | Computer Based | |
| 115 | MADHYA PRADESH | CHHINDWARA | Computer Based | |
| 116 | MADHYA PRADESH | GWALIOR | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 117 | MADHYA PRADESH | INDORE | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 118 | MADHYA PRADESH | JABALPUR | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 119 | MADHYA PRADESH | KHARGAON | Computer Based | |
| 120 | MADHYA PRADESH | MANDSUR | Computer Based | |
| 121 | MADHYA PRADESH | REWA | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 122 | MADHYA PRADESH | SAGAR | Computer Based | |
| 123 | MADHYA PRADESH | SATNA | Computer Based | |
| 124 | MADHYA PRADESH | SHAHDOL | Computer Based | |
| 125 | MADHYA PRADESH | UJJAIN | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 126 | MADHYA PRADESH | VIDISHA | Computer Based | |
| 127 | MAHARASHTRA | AHMEDNAGAR | Computer Based | |
| 128 | MAHARASHTRA | AKOLA | Computer Based | |
| 129 | MAHARASHTRA | AMRAVATI | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 130 | MAHARASHTRA | AURANGABAD | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 131 | MAHARASHTRA | BEED | Computer Based | |
| 132 | MAHARASHTRA | BHANDARA | Computer Based | |
| 133 | MAHARASHTRA | BHUSAWAL | Computer Based | |
| 134 | MAHARASHTRA | BULDANA | Computer Based | |
| 135 | MAHARASHTRA | CHANDRAPUR | Computer Based | |
| 136 | MAHARASHTRA | DHULE | Computer Based | |
| 137 | MAHARASHTRA | GADCHIROLI | Computer Based | |
| 138 | MAHARASHTRA | GONDIA | Computer Based | |
| 139 | MAHARASHTRA | JALGAON | Computer Based | |
| 140 | MAHARASHTRA | KOLHAPUR | Computer Based | |
| 141 | MAHARASHTRA | LATUR | Computer Based | |
| 142 | MAHARASHTRA | MUMBAI | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 143 | MAHARASHTRA | NAGPUR | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 144 | MAHARASHTRA | NANDED | Computer Based | |
| 145 | MAHARASHTRA | NASIK | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 146 | MAHARASHTRA | NAVI MUMBAI | Computer Based | |
| 147 | MAHARASHTRA | PARBHANI | Computer Based | |
| 148 | MAHARASHTRA | PUNE | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 149 | MAHARASHTRA | RAIGAD/ALIBAUG | Computer Based | |
| 150 | MAHARASHTRA | RATNAGIRI | Computer Based | |
| 151 | MAHARASHTRA | SANGALI | Computer Based | |
| 152 | MAHARASHTRA | SATARA | Computer Based | |
| 153 | MAHARASHTRA | SOLAPUR | Computer Based | |
| 154 | MAHARASHTRA | THANE | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 155 | MAHARASHTRA | WARDHA | Computer Based | |
| 156 | MAHARASHTRA | WASHIM | Computer Based | |
| 157 | MAHARASHTRA | YAVATMAL | Computer Based | |
| 158 | MANIPUR | IMPHAL | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 159 | MEGHALAYA | SHILLONG | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 160 | MIZORAM | AIZAWL | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 161 | NAGALAND | DIMAPUR | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 162 | NAGALAND | KOHIMA | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 163 | ODISHA | ANGUL | Computer Based | |
| 164 | ODISHA | BALASORE | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 165 | ODISHA | BERHAMPUR | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 166 | ODISHA | BHUBANESWAR | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 167 | ODISHA | CUTTACK | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 168 | ODISHA | JEYPORE | Computer Based | |
| 169 | ODISHA | ROURKELA | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 170 | ODISHA | SAMBALPUR | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 171 | PUDUCHERRY | PUDUCHERRY | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 172 | PUNJAB | AMRITSAR | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 173 | PUNJAB | BHATINDA | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 174 | PUNJAB | FATHEGARH | Computer Based | |
| 175 | PUNJAB | JALANDHAR | Computer Based | |
| 176 | PUNJAB | LUDHIANA | Computer Based | |
| 177 | PUNJAB | PATHANKOT | Computer Based | |
| 178 | PUNJAB | PATIALA | Computer Based | |
| 179 | PUNJAB | PHAGWARA | Computer Based | |
| 180 | PUNJAB | ROPAR | Computer Based | |
| 181 | PUNJAB | SANGRUR | Computer Based | |
| 182 | RAJASTHAN | AJMER | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 183 | RAJASTHAN | ALWAR | Computer Based | |
| 184 | RAJASTHAN | BHARATPUR | Computer Based | |
| 185 | RAJASTHAN | BHILWARA | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 186 | RAJASTHAN | BIKANER | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 187 | RAJASTHAN | JAIPUR | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 188 | RAJASTHAN | JODHPUR | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 189 | RAJASTHAN | KOTA | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 190 | RAJASTHAN | SIKAR | Computer Based | |
| 191 | RAJASTHAN | UDAIPUR | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 192 | SIKKIM | GANGTOK | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 193 | TAMIL NADU | CHENNAI | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 194 | TAMIL NADU | COIMBATORE | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 195 | TAMIL NADU | CUDDALORE | Computer Based | |
| 196 | TAMIL NADU | DINDIGUL | Computer Based | |
| 197 | TAMIL NADU | KANYAKUMARI | Computer Based | |
| 198 | TAMIL NADU | KARUR | Computer Based | |
| 199 | TAMIL NADU | MADURAI | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 200 | TAMIL NADU | NAMAKKAL | Computer Based | |
| 201 | TAMIL NADU | SALEM | Computer Based | |
| 202 | TAMIL NADU | TANJORE | Computer Based | |
| 203 | TAMIL NADU | THIRUVANNAMALAI | Computer Based | |
| 204 | TAMIL NADU | THOOTHUKUDI | Computer Based | |
| 205 | TAMIL NADU | TIRUCHIRAPPALLI | Computer Based | |
| 206 | TAMIL NADU | TIRUNELVELI | Computer Based | |
| 207 | TAMIL NADU | VELLORE | Computer Based | |
| 208 | TAMIL NADU | VILLIPURAM | Computer Based | |
| 209 | TAMIL NADU | VIRUDHUNAGAR | Computer Based | |
| 210 | TELANGANA | HYDERABAD | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 211 | TELANGANA | KARIMNAGAR | Computer Based | |
| 212 | TELANGANA | KHAMMAM | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 213 | TELANGANA | MAHABUBNAGAR | Computer Based | |
| 214 | TELANGANA | NALGONDA | Computer Based | |
| 215 | TELANGANA | WARANGAL | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 216 | TRIPURA | AGARTALA | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 217 | UTTAR PRADESH | AGRA | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 218 | UTTAR PRADESH | ALIGARH | Computer Based | |
| 219 | UTTAR PRADESH | ALLAHABAD | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 220 | UTTAR PRADESH | BAREILLY | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 221 | UTTAR PRADESH | BULANDSHAHAR | Computer Based | |
| 222 | UTTAR PRADESH | FAIZABAD | Computer Based | |
| 223 | UTTAR PRADESH | GHAZIABAD | Computer Based | |
| 224 | UTTAR PRADESH | GORAKHPUR | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 225 | UTTAR PRADESH | GREATER NOIDA/NOIDA | Computer Based | |
| 226 | UTTAR PRADESH | JHANSI | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 227 | UTTAR PRADESH | KANPUR | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 228 | UTTAR PRADESH | LUCKNOW | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 229 | UTTAR PRADESH | MATHURA | Computer Based | |
| 230 | UTTAR PRADESH | MEERUT | Computer Based | |
| 231 | UTTAR PRADESH | MORADABAD | Computer Based | |
| 232 | UTTAR PRADESH | MUZAFFARNAGAR | Computer Based | |
| 233 | UTTAR PRADESH | SITAPUR | Computer Based | |
| 234 | UTTAR PRADESH | VARANASI | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 235 | UTTARAKHAND | DEHRADUN | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 236 | UTTARAKHAND | HALDWANI | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 237 | UTTARAKHAND | HARIDWAR | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 238 | UTTARAKHAND | PANTNAGAR | Computer Based | |
| 239 | UTTARAKHAND | ROORKEE | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 240 | WEST BENGAL | ASANSOL | Computer Based | |
| 241 | WEST BENGAL | BARDHMAN | Computer Based | |
| 242 | WEST BENGAL | DURGAPUR | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 243 | WEST BENGAL | HALDIA | Computer Based | |
| 244 | WEST BENGAL | HOOGHLY | Computer Based | |
| 245 | WEST BENGAL | HOWRAH | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 246 | WEST BENGAL | KALYANI | Computer Based | |
| 247 | WEST BENGAL | KOLKATA | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 248 | WEST BENGAL | SILIGURI | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 249 | OUTSIDE INDIA | COLOMBO | Computer Based | |
| 250 | OUTSIDE INDIA | KATHMANDU | Computer Based | |
| 251 | OUTSIDE INDIA | SINGAPORE | Computer Based | |
| 252 | OUTSIDE INDIA | BAHRAIN | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 253 | OUTSIDE INDIA | DUBAI | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 254 | OUTSIDE INDIA | MUSCAT | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 255 | OUTSIDE INDIA | RIYADH | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 256 | OUTSIDE INDIA | SHARJAH | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 257 | OUTSIDE INDIA | QATAR | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
| 258 | OUTSIDE INDIA | DHAKA | Pen Paper based | Computer Based |
REMARKS:
1. The candidates may note that Paper-2 (B. Arch./B. Planning.) will be conducted on 08/04/2018 from 2.00PM to 5.00PM(IST), only in Pen & Paper based examination cities and also in Colombo, Kathmandu, Singapore, Dhaka.
2. The Computer Based Examination for Paper – 1 in Colombo, Dhaka, Kathmandu, Singapore, Bahrain, Dubai, Muscat, Riyadh, Sharjah & Qatar will be held on 15th April 2018.
Appendix 3
LIST OF QUALIFYING EXAMINATIONS
- The final examination of the 10+2 system, conducted by any recognized central/ state Board, such as Central Board of Secondary Education, New Delhi; Council for the Indian School Certificate Examinations, New Delhi; etc.
- Intermediate or two-year Pre-University examination conducted by a recognized Board/ University.
- Final examination of the two-year course of the Joint Services Wing of the National Defence Academy.
- Senior Secondary School Examination conducted by the National Institute of Open Schooling with a minimum of five subjects.
- Any Public School/ Board/ University examination in India or in any foreign country recognized as equivalent to the 10+2 system by the Association of Indian Universities (AIU).
- H.S.C. vocational examination. [Only for Admission to IITs]
- A Diploma recognized by AICTE or a state board of technical education of at least 3 year duration. [Only for Admission to IITs]
- General Certificate Education (GCE) examination (London/Cambridge/Sri Lanka) at the Advanced (A) level. [Only for Admission to IITs]
- High School Certificate Examination of the Cambridge University or International Baccalaureate Diploma of the International Baccalaureate Office, Geneva. [Only for Admission to IITs]
In case the relevant QE is not a public examination, the candidate must have passed at least one public (Board or Pre-University) examination at an earlier level.[Only for Admission to IITs]
Appendix 4
STATE CODE OF ELIGIBILITY
| NAME OF THE STATE /UT | CODE |
| Andaman & Nicobar Islands (UT) | 01 |
| Andhra Pradesh | 02 |
| Arunachal Pradesh | 03 |
| Assam | 04 |
| Bihar | 05 |
| Chandigarh (UT) | 06 |
| Chhattisgarh | 07 |
| Dadra & Nagar Haveli (UT) | 08 |
| Daman & Diu (UT) | 09 |
| Delhi | 10 |
| Goa | 11 |
| Gujarat | 12 |
| Haryana | 13 |
| Himachal Pradesh | 14 |
| Jammu & Kashmir | 15 |
| Jharkhand | 16 |
| Karnataka | 17 |
| Kerala | 18 |
| Lakshadweep (UT) | 19 |
| Madhya Pradesh | 20 |
| Maharashtra | 21 |
| Manipur | 22 |
| Meghalaya | 23 |
| Mizoram | 24 |
| Nagaland | 25 |
| Odisha | 26 |
| Puducherry (UT) | 27 |
| Punjab | 28 |
| Rajasthan | 29 |
| Sikkim | 30 |
| Tamil Nadu | 31 |
| Tripura | 32 |
| Uttar Pradesh | 33 |
| Uttarakhand | 34 |
| West Bengal | 35 |
| Telangana | 36 |
| Foreign/OCI/PIO/ Nepal / Bhutan | 98 |
Appendix 5
TENTATIVE LIST OF PARTICIPATING INSTITUTIONS IN CENTRALISED SEAT ALLOCATION PROCESS
National Institutes of Technology (NITs)
- National Institute of Technology , Agartala (Tripura)
- Motilal Nehru National Institute of Technology, Allahabad (U.P.)
- National Institute of Technology, Arunachal Pradesh.
- Maulana Azad National Institute of Technology, Bhopal (MP)
- National Institute of Technology, Calicut (Kerela)
- National Institute of Technology, Delhi
- National Institute of Technology, Durgapur (West Bengal)
- National Institute of Technology, Goa
- National Institute of Technology, Hamirpur (Himachal Pradesh)
- Malviya National Institute of Technology, Jaipur (Rajasthan)
- Dr. B R Ambedkar National Institute of Technology, Jalandhar (Punjab)
- National Institute of Technology, Jamshedpur (Jharkhand)
- National Institute of Technology, Kurukshetra (Haryana)
- National Institute of Technology, Manipur
- National Institute of Technology, Meghalaya
- National Institute of Technology, Mizoram
- National Institute of Technology, Nagaland
- Visvesvaraya National Institute of Technology, Nagpur (Maharashtra)
- National Institute of Technology, Patna (Bihar)
- National Institute of Technology, Puducherry
- National Institute of Technology, Raipur (Chhattisgarh)
- National Institute of Technology, Rourkela (Odisha)
- National Institute of Technology, Sikkim
- National Institute of Technology, Silchar (Assam)
- National Institute of Technology, Hazartbal, Srinagar (J & K)
- Sardar Vallabhbhai National Institute of Technology, Surat (Gujarat)
- National Institute of Technology, Surathkal, Mangalore (Karnataka)
- National Institute of Technology, Tiruchirapalli (Tamil Nadu)
- National Institute of Technology, Uttrakhand
- National Institute of Technology, Warangal
- National Institute of Technology, Andhra Pradesh, Vatluru, Eluru – 534007
Indian Institutes of Information Technology (IIITs, IIITM & IIITDM)
- Atal Bihari Vajpayee Indian Institute of Information Technology & Management, Gw
- Indian Institute of Information Technology, Design & Manufacturing, Kanchipuram,
- Indian Institute of Information Technology, Jhalwa, Allahabad (UP)
- Pandit Dwarka Prasad Mishra Indian Institute of Information Technology, Design &
- Indian Institute of Information Technology, Guwahati (Assam)
- Indian Institute of Information Technology, Kota (Rajasthan)
- Indian Institute of Information Technology, Sri City, Chitoor (A. P.)
- Indian Institute of Information Technology, Vadodara (Gujarat)
- Indian Institute of Information Technology Manipur Mantripukhri, Imphal 795001
- Indian Institute of Information Technology Srirangam,Tiruchirappalli
- Indian Institute of Information Technology Lucknow
- Indian Institute of Information Technology(IIIT) Dharwad
- Indian Institute of Information Technology(IIIT) Kurnool
- Indian Institute of Information Technology(IIIT) Kottayam
- Indian Institute of Information Technology(IIIT) Kalyani, West Bengal
- Indian Institute of Information Technology(IIIT) Kilohrad, Sonepat, Haryana
- Indian Institute of Information Technology(IIIT) Una, Himachal Pradesh
- Indian Institute of Information Technology (IIIT) Ranchi, Jharkhand
- Indian Institute of Information Technology (IIIT) Nagpur, Maharashtra
- Indian Institute of Information Technology (IIIT) Pune , Maharshtra
- Indian Institute of Information Technology Bhagalpur
- Indian Institute of Information Technology Bhopal
- Indian Institute of Information Technology Surat
Other Central Government/State Government Funded Institutions
- Assam University, Silchar (Assam)
- Birla Institute of Technology, Mesra, Ranchi (Jharkhand)
- Gurukul Kangri Vishwavidyalaya, Haridwar (Uttarakhand)
- Indian Institute of Carpet Technology, Bhadohi (U.P.)
- Institute of Infrastructure, Technology, Research & Management, Ahmedabad
- Institute of Technology, Guru Ghasidas Vishawavidyalaya, Bilaspur (C.G.)
- J.K. Institute of Applied Physics & Technology, University of Allahabad, Allahabad- 211002 (U.P.)
- Mizoram University, Aizwal-796009
- National Institute of Foundry& Forge Technology, P.O. Hatia, Ranchi (Jharkhand).
- School of Planning and Architecture, Bhopal (Madhya Pradesh)
- School of Planning and Architecture, I.P. Estate, New Delhi (SPA, Delhi).
- School of Planning and Architecture, Vijayawada (Andhra Pradesh)
- Shri Mata Vaishno Devi University, Katra-182320 (J & K)
- Tezpur University, NAPAAM, Tezpur (Assam)
- Indian Institute of Engineering Science & Technology, Shibpur, Distt Howrah (Formerly
- Indian Institute of Crop Processing Technology, Thanjavur, Tamilnadu
- National Institute of Electronics and Information Technology, Aurangabad, Maharashtra
- Sant Longowal Institute of Engineering and Technology Longowal – 148106, Distt. Sangr
- Harcourt Butler Technical University, Kanpur (U.P.)
- Indian Institute of Petroleum & Energy, Visakhapatnam.
- Indian Institute of Handloom Technology, Salem, Tamil Nadu.
- Jamia Hamdard University, Delhi.
- University of Hyderabad, Hyderabad
Many States/Institutes used JEE (MAIN) -2017 ranks to fill seats through their own Seat Allocation Process are listed here.
- Haryana
- Madhya Pradesh
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Uttarakhand
- Punjab Technical University, Jalandhar
- Punjab Engineering College, Chandigarh
- Indian Institute of Science, Banglore
- Indian Institute of Space Technology, Thiruvanathapuram
- Indraprastha Institute of Information Technology, Delhi
- Delhi Technological University, New Delhi.
- Indira Gandhi Delhi Technical University for Women, New Delhi.
- Netaji Subhash Institute of Technology (under Delhi University).
- Jamia Millia Islamia, New Delhi.
Tentative list of Self Financed Deemed Universities/Universities/Other Institutions participating in CENTRAL SEAT ALLOCATION BOARD (CSAB) through JEE (Main).
(Eligible only for Spot Round)
- AISECT UNIVERSITY, BHOPAL, MADHYA PRADESH
- AMITY SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING, AMITY UNIVERSITY HARYANA, GURGAON, HARYANA
- AMITY SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING, AMITY UNIVERSITY MADHYA PRADESH, GWALIOR, MADHYA PRADESH
- AMITY SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING, AMITY UNIVERSITY MUMBAI, MAHARASHTRA
- AMITY SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING, AMITY UNIVERSITY RAJASTHAN, JAIPUR, RAJASTHAN
- AMITY SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING, AMITY UNIVERSITY UTTAR PRADESH, LUCKNOW, UTTAR PRADESH
- AMITY SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING, AMITY UNIVERSITY UTTAR PRADESH, NOIDA, UTTAR PRADESH
- AMITY SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING, AMITY UNIVERSITY WEST BENGAL, KOLKATA, WEST BENGAL
- AMITY SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING, GREATER NOIDA, UTTAR PRADESH
- AMITY SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING, RAIPUR, CHHATTISGARH
- BHAGWANT UNIVERSITY,SIKAR ROAD,AJMER, RAJASTHAN
- Dr. M.G.R. EDUCATIONAL AND RESEARCH INSTITUTE, CHENNAI, TAMIL NADU
- DR. K.N. MODI UNIVERSITY, TONK, RAJASTHAN
- GALGOTIAS UNIVERSITY UTTAR PRADESH, GREATER NOIDA, UTTAR PRADESH
- ITM UNIVERSITY GWALIOR, MADYA PRADESH
- KALASALINGAM ACADEMY OF RESEARCH AND EDUCATION, ANAND NAGAR, KRISHNANKOI
- NOIDA INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY, GAUTAM BUDH NAGAR, UTTAR PRADESH
- PERIYAR MANIAMMAI INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY, VALLAM THANJAVUR,
- TECHNO INDIA UNIVERSITY, KOLKATA, WEST BENGAL (RESIDENTIAL)
Final List of Institutions admitting students (with intake in each discipline and category as per reservation) through JEE (Main)-2018 shall be available on the website of SEAT ALLOCATION BOARD in the month of May/June 2018.
Appendix 6
BOARDS/UNIVERSITIESCONDUCTING CLASS 12TH/EQUIVALENT EXAMINATION
1. ANDHRA PRADESH BOARD OF INTERMEDIATE EDUCATION
2. ASSAM HIGHER SECONDARY EDUCATION COUNCIL
3. BIHAR INTERMEDIATE EDUCATION COUNCIL(BIHAR SCHOOL EXAMINATION BOARD)
4. CENTRAL BOARD OF SECONDARY EDUCATION
5. CHATTISGARH MADHYAMIK SHIKSHA MANDAL (CHATTISGARH BOARD OF SECONDARY EDUCATION)
6. COUNCIL FOR THE INDIAN SCHOOL CERTIFICATE EXAMINATIONS
7. GOA BOARD OF SECONDARY AND HIGHER SECONDARY EDUCATION
8. GUJARAT SECONDARY EDUCATION BOARD
9. HARYANA BOARD OF EDUCATION
10. H P BOARD OF SCHOOL EDUCATION
11. J AND K STATE BOARD OF SCHOOL EDUCATION
12. JHARKHAND ACADEMIC COUNCIL
13. KARNATAKA BOARD OF PRE UNIVERSITY EDUCATION
14. KERALA BOARD OF PUBLIC EXAMINATIONS
15. MADHYA PRADESH BOARD OF SECONDARY EDUCATION
16. MAHARASTRA STATE BOARD OF SECONDARY AND HIGHER SECONDARY EDUCATION
17. MANIPUR COUNCIL OF HIGHER SECONDARY EDUCATION
18. MEGHALAYA BOARD OF SECONDARY EDUCATION
19. MIZORAM BOARD OF SCHOOL EDUCATION
20. NAGALAND BOARD OF SCHOOL EDUCATION
21. ODISHA COUNCIL OF HIGHER SECONDARY EDUCATION
22. PUNJAB SCHOOL EDUCATION BOARD
23. RAJASTHAN BOARD OF SECONDARY EDUCATION
24. TAMIL NADU BOARD OF HIGHER SECONDARY EDUCATION
25. TRIPURA BOARD OF SECONDARY EDUCATION
26. U P BOARD OF HIGH SCHOOL AND INTERMEDIATE EDUCATION
27. UTTARANCHAL SHIKSHA EVAM PARIKSHA PARISHAD
28. WEST BENGAL COUNCIL OF HIGHER SECONDARY EDUCATION
29. NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF OPEN SCHOOLING
30. JAMIA MILIA ISLAMIA, NEW DELHI
31. ALIGARH MUSLIM UNIVERSITY, ALIGARH
32. DAYALBAGH EDUCATIONAL INSTITUTE, AGRA
33. BANASTHALI VIDYAPEETH, RAJASTHAN
34. VISHWA BHARTI UNIVERSITY, SHANTINIKETAN, BIRBHOOM, WB
35. RAJIV GANDHI UNIVERSITY OF KNOWLEDGE TECHNOLOGIES, HYDERABAD
36. HARYANA OPEN SCHOOL, BHIWANI
37. RAJASTHAN STATE OPEN SCHOOL, JAIPUR
38. M P STATE OPEN SCHOOL, BHOPAL
39. ANDHRA PRADESH OPEN SCHOOL SOCIETY
40. BIHAR BOARD OF OPEN SCHOOLING EXAMINATION
41. CHHATTISGARH STATE OPEN SCHOOL
42. CBSE i (CBSE international)
43. TELANGANA BOARD OF INTERMEDIATE EDUCATION
44. TELANGANA PRADESH OPEN SCHOOL SOCIETY
45. WEST BENGAL COUNCIL OF RABINDRA OPEN SCHOOLING
46. ASSAM STATE OPEN SCHOOL
47. DIRECTORATE GENERAL OF MILITARY TRAINING (RIMC)
81. BHUTAN HIGHER SECONDARY EDUCATION CERTIFICATE
82. ‘A’ LEVEL OF GENERAL CERTIFICATE OF EDUCATION, CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY (IGSE)
83. INTERNATIONAL BACCALAUREATE
84. EDEXCEL, LONDON (UK)
85. HIGHER SECONDARY EDUCATION BOARD, NEPAL
98. TECHNICAL/VOCATIONAL BOARD
99. OTHER BOARD
Appendix 7

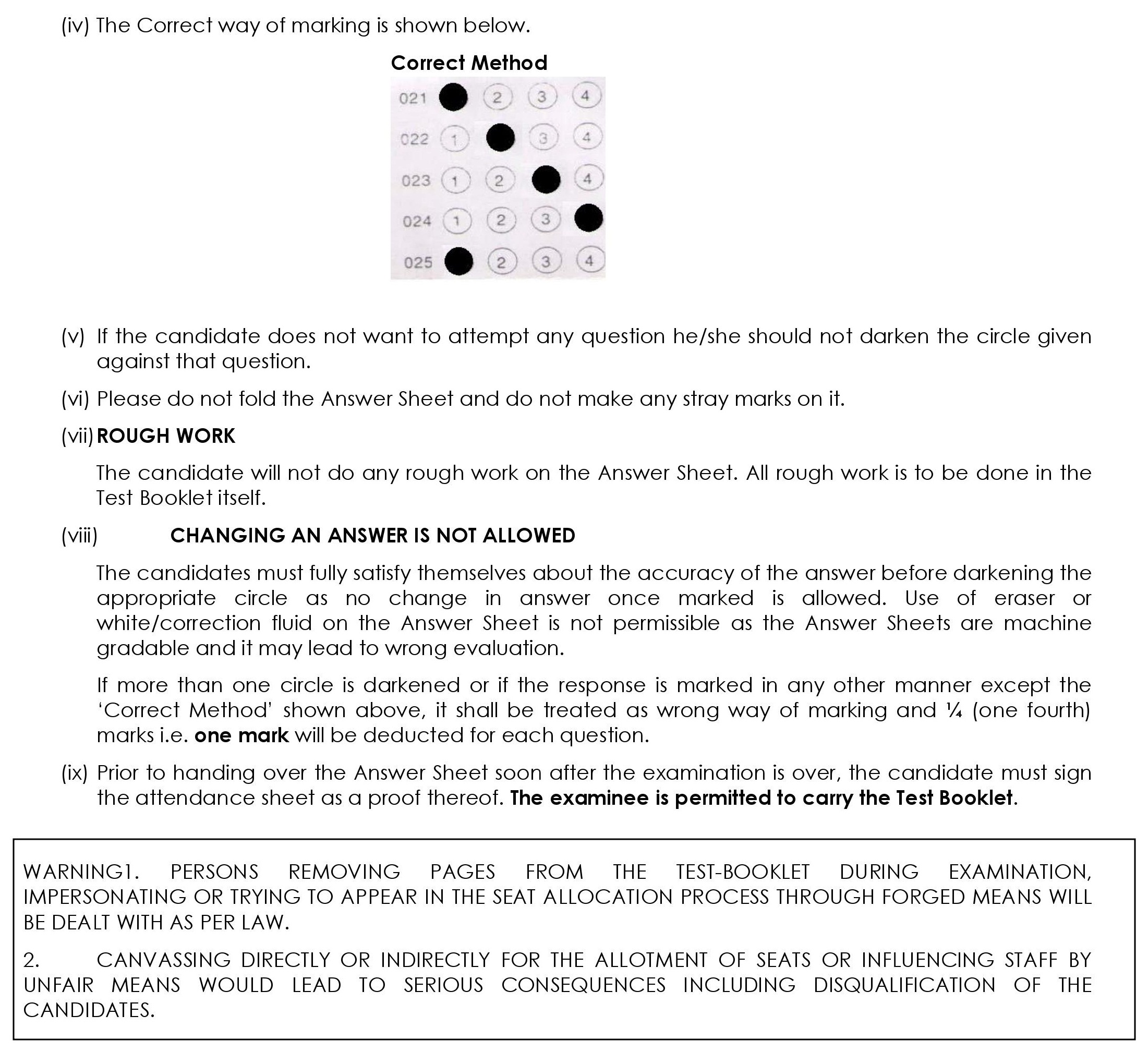
Appendix 8
TIME SCHEDULE FOR JEE (Main) – 2018
(A) TIME SCHEDULE FOR Pen and Paper based examination
| Paper-1(B.E./B.Tech.) | Paper-2(B.Arch./B. Planning.) | |
| DATES OF EXAMINATION | 08.04.2018 (Sunday) | 08.04.2018 (Sunday) |
| a) Entry in the Examination Centre | 0700 HRS. (IST) | 1300 HRS. (IST) |
| b) Entry in the Examination Hall | 0900 HRS. (IST) | 1330 HRS. (IST) |
| c) Distribution of Test Booklet | 0920 HRS. (IST) | 1350 HRS. (IST) |
| d) Seal of the Test Booklet to be broken/opened to take out the Answer Sheet |
0925 HRS. (IST) | 1355 HRS. (IST) |
| e) Last entry in the Examination Hall | 0930 HRS. (IST) | 1400 HRS. (IST) |
| f) Test commences | 0930 HRS. (IST) | 1400 HRS. (IST) |
| g) Test concludes | 1230 HRS. (IST) | 1700 HRS. (IST) |
(B) TIME SCHEDULE FOR COMPUTER BASED EXAMINATION
| DATES OF EXAMINATION FOR PAPER-1 (B. E./B. TECH.): 15th& 16thApril 2018 | ||
| Morning Session | Afternoon session* | |
| a) Entry in the Examination Centre | 0700 HRS. (IST) | 1300 HRS. (IST) |
| b) Entry in the Examination Hall | 0900 HRS. (IST) | 1330 HRS. (IST) |
| c) Last entry in the Examination Hall | 0930 HRS. (IST) | 1400 HRS. (IST) |
| d) Test commences | 0930 HRS. (IST) | 1400 HRS. (IST) |
| e) Test concludes | 1230 HRS. (IST) | 1700 HRS. (IST) |
* If required.
APPENDIX 9



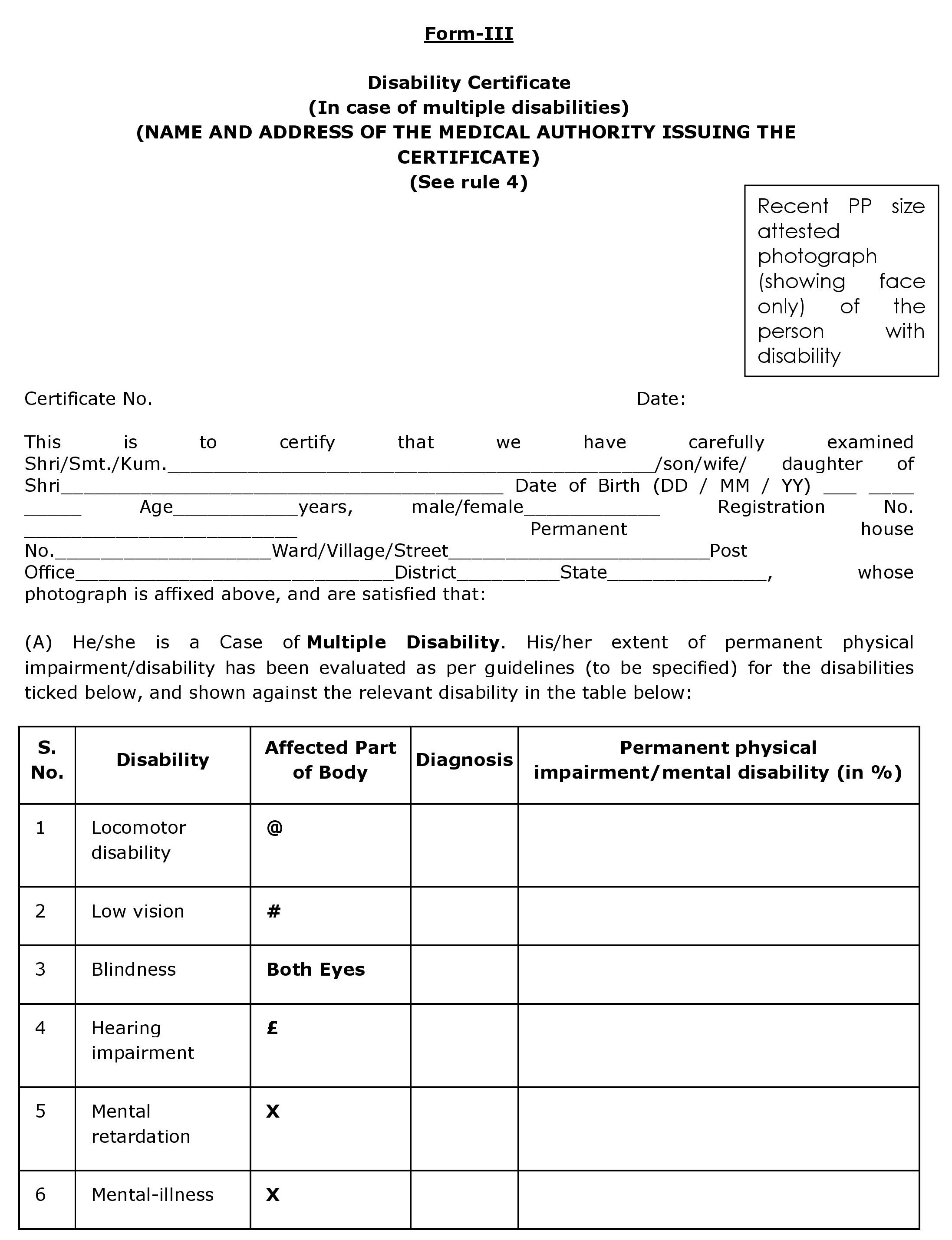

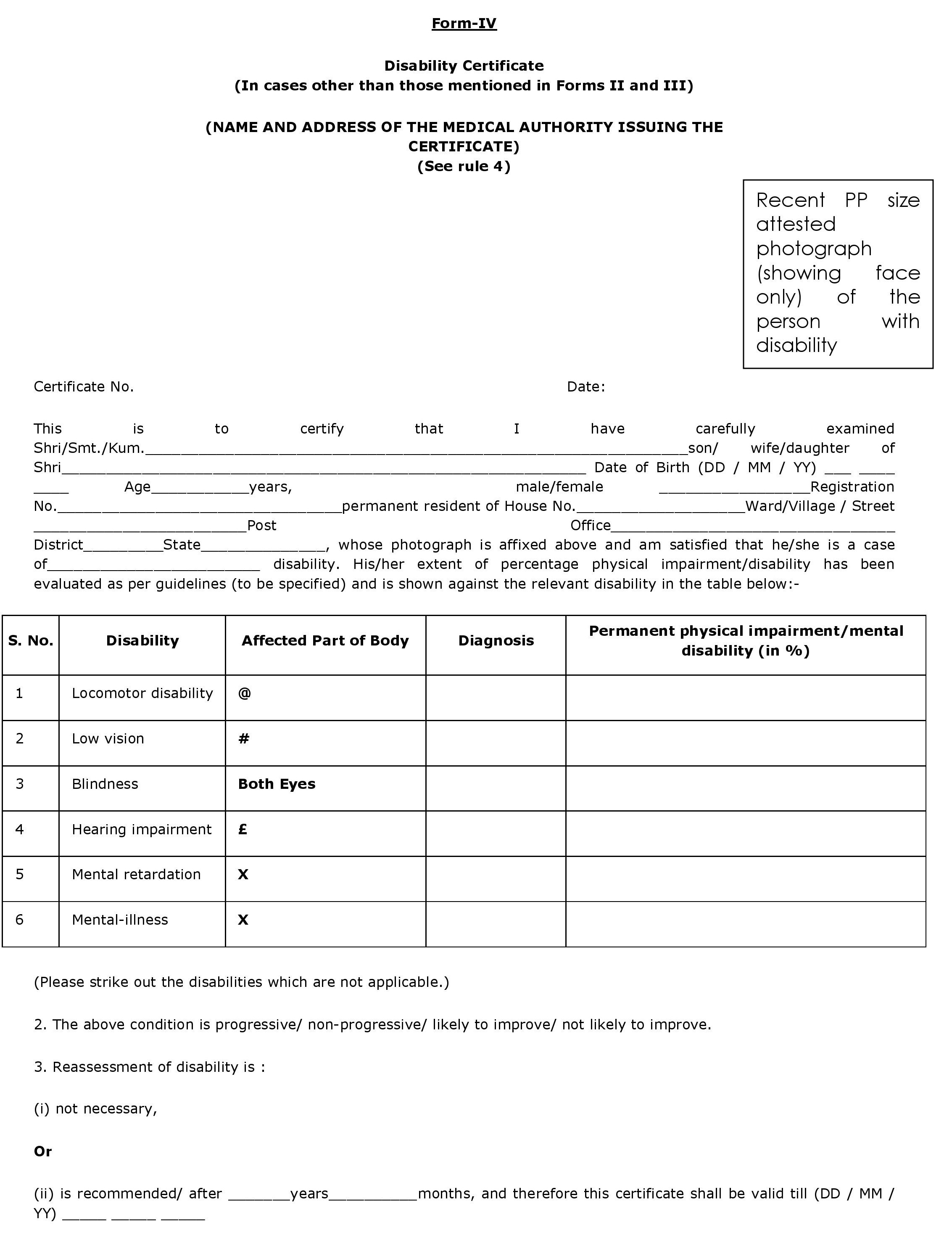

IMPORTANT INFORMATION AT A GLANCE
| 1 | a. Dates of JEE (Main) for Pen and Paper Based examination 08.04.2018 (Sunday) | PAPER – 1 (B.E./B.Tech.) PAPER – 2 (B.Arch./B. Planning) |
0930-1230 hrs (IST) 1400-1700 hrs (IST) |
| b. Date of JEE (Main) (Computer Based Examination) | 15/04/2018 (Sunday) 16/04/2018 (Monday) |
||
| c. Online submission of application on website www.jeemain.nic.in | 01.12.2017 – 01.01.2018 | ||
| 2 | Last date forOnline submission of applications | 01.01.2018 | |
| 3 | Date of Availability of Admit Card for JEE (Main) on Website | 2nd week of March 2018 onwards | |
| 4 | Centre of Examination | As indicated on the Admit Card | |
| 5. | Display of Answer key and image of response (OMR) sheet | 24th – 27th April, 2018 | |
| 6 | Declaration of JEE (Main) Paper–1 Score / All India Rank and top 220000 candidates eligible for appearing in JEE (Advanced) | 30th April, 2018 | |
| 7 | Declaration of All India Rank JEE (Main) Paper – 2. | 31st May, 2018 | |
| 8 | Availability of Score/Rank Cards on website | After declaration of All India Rank (AIR) of JEE (Main)-2018 | |
| 9 | Materials to be brought on the day of examination | Admit Card and document as required under point no. 7.However, the candidates who have also opted forPaper-2 (B. Arch./B. Planning.) of JEE (Main), are advised to bring their own clipboard, geometry box set, pencils, erasers and colour pencils or crayons. | |
| 10 | Rough Work (Pen and Paper Based Examination) Rough Work (Computer Based Examination) |
All rough work is to be done in the Test Booklet only. Thecandidate should NOT do any rough work or put stray mark on the Answer Sheet.Paper for Rough work will be provided at the examinationcentre | |
